Looking to run a Linux or Windows operating system for specific tasks? You can either dual-boot both operating systems or install the one you need in a Virtual Machine. In this guide, we’ll explore GNOME Boxes, a popular Virtualization program. There are even different Virtual Machine managing programs that you could use to add a different operating system to your OS.
There’s VirtualBox and there’s also QEMU, the two of the most famous Virtualization software, however, there are even other Virtualization programs developed by the Desktop Environments such as the GNOME team’s GNOME Boxes.
In this article, we will take a closer look at the implementation and installation of this Virtualization program, which is part of the GNOME project.
GNOME Boxes is a user-friendly Virtualization Software developed by the GNOME team. It allows users to install various Linux distributions directly, customize settings like IP address, CPU cores, disk space, and RAM, and even take snapshots of the OS. With features like Express Installation and automatic screen resolution detection, GNOME Boxes provides a seamless experience for managing virtual machines
System Requirements for Running GNOME Boxes
- GNOME Boxes lets you run virtual machines on your computer. It sets aside up to 20GB of storage space for each virtual machine, but don’t worry – the actual disk space used will be less than or equal to whatever the virtual machine itself takes up.
- You’ll need at least 500MB of RAM to run GNOME Boxes, but for best performance, we recommend having at least 8GB.
- Your computer’s processor should support hardware virtualization extensions, and these should be switched on in your system’s BIOS settings. This allows GNOME Boxes to run much more efficiently.
- It’s also a good idea to have around 20GB of free disk space on your computer before running GNOME Boxes and creating any virtual machines. This free space allows the program to operate smoothly
How to Install GNOME Boxes on Various Linux Distributions
If any Linux distribution ships the Vanilla GNOME, then there’s a high chance that ‘GNOME boxes’ is already installed on your system. However, if it isn’t then you can easily install it on every Linux distribution because it is available in the official repositories directly from the Terminal window by typing the following command as per your Linux distribution:
# On Debian and Ubuntu based distributions:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install gnome-boxes
# On Fedora Workstation:
sudo dnf install gnome-boxes
# On Arch Linux based distributions:
sudo pacman -S gnome-boxes
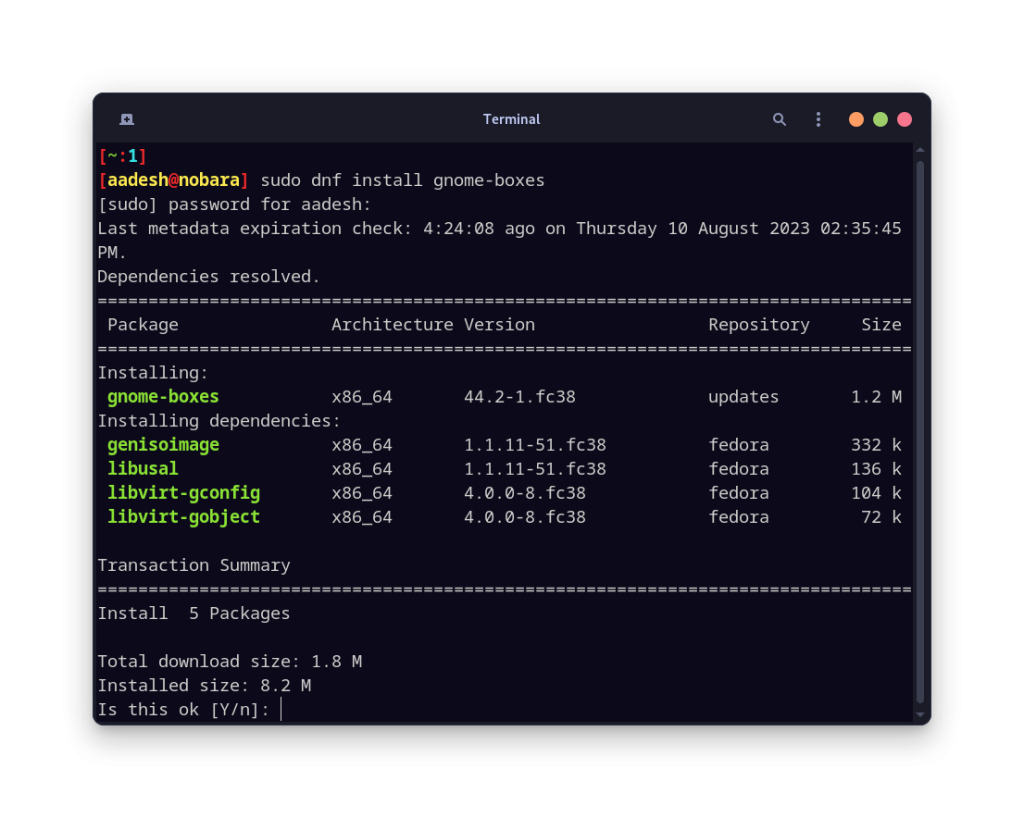
If you want to install the sandboxed version of this VM manager on your system, then you can go with the Flatpak version of this application:
flatpak install flathub org.gnome.Boxes
Once installed, you can launch it from your App Grid/Menu on your desktop.
Explore the Features of GNOME Boxes
GNOME Boxes offers a robust set of features essential for Virtualization Software. Here’s an overview of what you can expect:
- With GNOME Boxes, you don’t have to download the ISO file of any major Linux distribution such as RHEL, CentOS openSUSE, Ubuntu, Debian, and NixOS. Most of them are already mentioned in the application and can be downloaded directly.
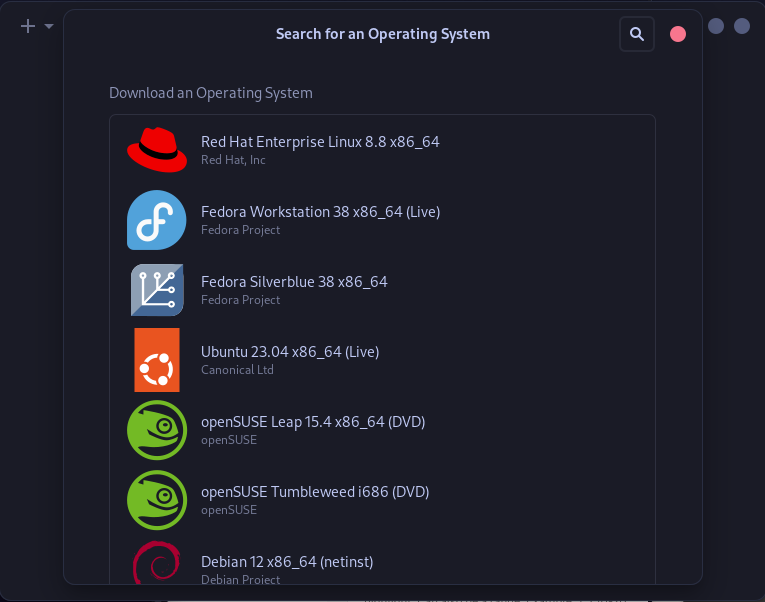
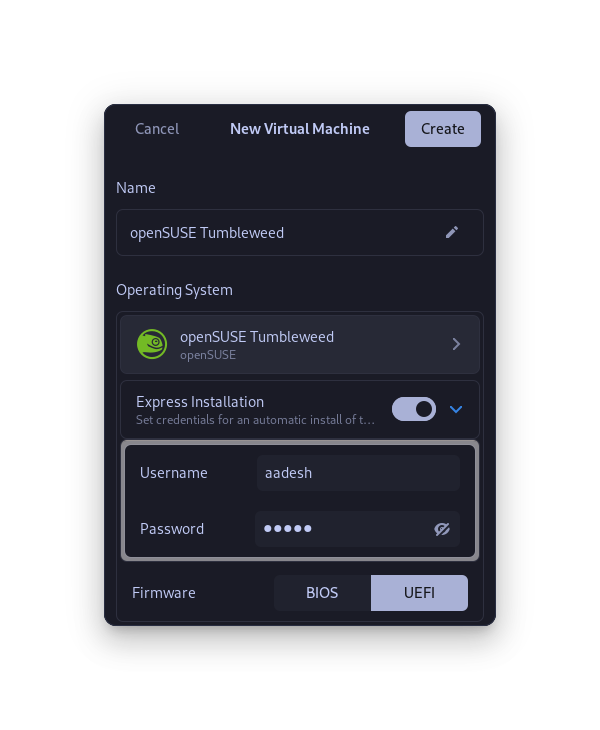
- The Express Installation feature allows you to set up a username and a password directly to the downloaded ISO which helps the time it takes to install an OS drastically.
- GNOME boxes can automatically detect your screen resolution (in both Windowed and Full-screen mode) and set the correct resolution to the installed Operating System.
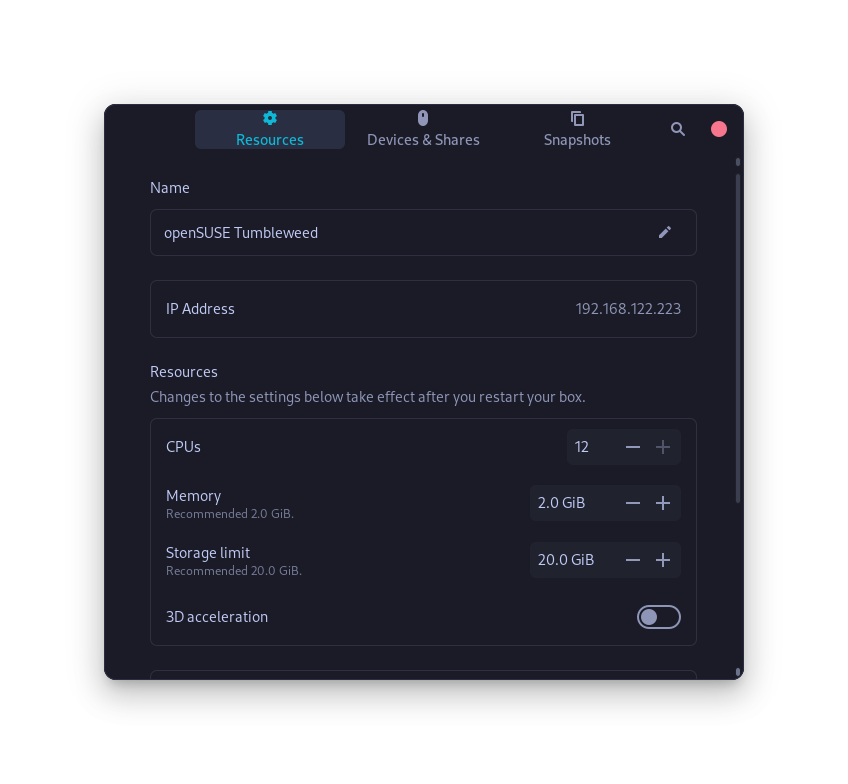
- Allows you to customize the IP address of the VM as well as a folder and Bluetooth device pass-through.
- If you want to share files from your current OS to the operating system installed in a VM, you can do that by simply dragging the files and dropping it into the open folder in the OS.
- Features like changing the allotted CPU cores, increasing or decreasing allotted disk space and RAM is also built into the OS.
- You can also take snapshots of the OS at different times, which essentially act as a backup in case you mess something up. You can always restore your OS from the Snapshots.
Wrapping Up: Is it the right option for you?
GNOME Boxes might certainly be the best GUI Virtualization software out there for users who are looking for a ‘just works’ application. While Virt-Manager and QEMU require you to enable certain SystemD daemons and download the ISO of your distribution to work, GNOME boxes do not need any of those things. But of course, not all the Linux distributions are mentioned in this application, and you will have to get an ISO from the Internet if you want to try and obscure Linux distribution. Distributions like Manjaro, Alma, Rocky, Alpine, and NixOS are available in the list, but not Endeavor OS or even Linux Mint which are quite famous in desktop Linux usage.





