Kafka is the high-performance TCP protocol server used for large distribution of servers to clients. It is used to collect, store, retrieve, and scale large amounts of data. One of the prior advantages of this technology, Kafka, is that it streams massive messages in Low Latency. Kafka is written in Java and Scala. It can be deployed as bare hardware, virtual machines, and containers as well as in cloud environments.
What You’ll Learn
The main objective of this article is to learn the commands used to install the kafkactl in a Linux machine, a versatile command line tool used to streamline management and interaction with the Apache kafka cluster. By the end of this article, you will be well efficient in monitoring the Apache kafka cluster using your command line .
Prerequisites for Installation
Hardware requirements
A Linux-based operating system for example Ubuntu, CentOS, running on the host machine.
Software Dependencies
- Java Development kit(JDK) – Here’s a tutorial on installing Java on Ubuntu.
- A functioning Apache kafka up and running
- Access to the command line terminal
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Kafkactl on Linux
Before installing Kafkactl we must make sure of the following things:
Check the Version of Java Installed
Check the version of Java using the following commands:
java --version
If there is no Java development kit present follow the commands to install it on your machine
Installing the Latest Java on Linux
The first thing is to update your machine and the following command will update your machine to the current version that it supports:
sudo apt install default- jdk
Next, you have to install JDK in your local system using the following command:
sudo apt install default- jdk
Note: Remember, if you give invalid file names for installation error may occur saying “unable to locate the file”. So, check the file names properly and install the packages.
Install Kafkactl in Linux
Step 1: Navigate to the official site of Kafka and download the Kafka latest release file from here .
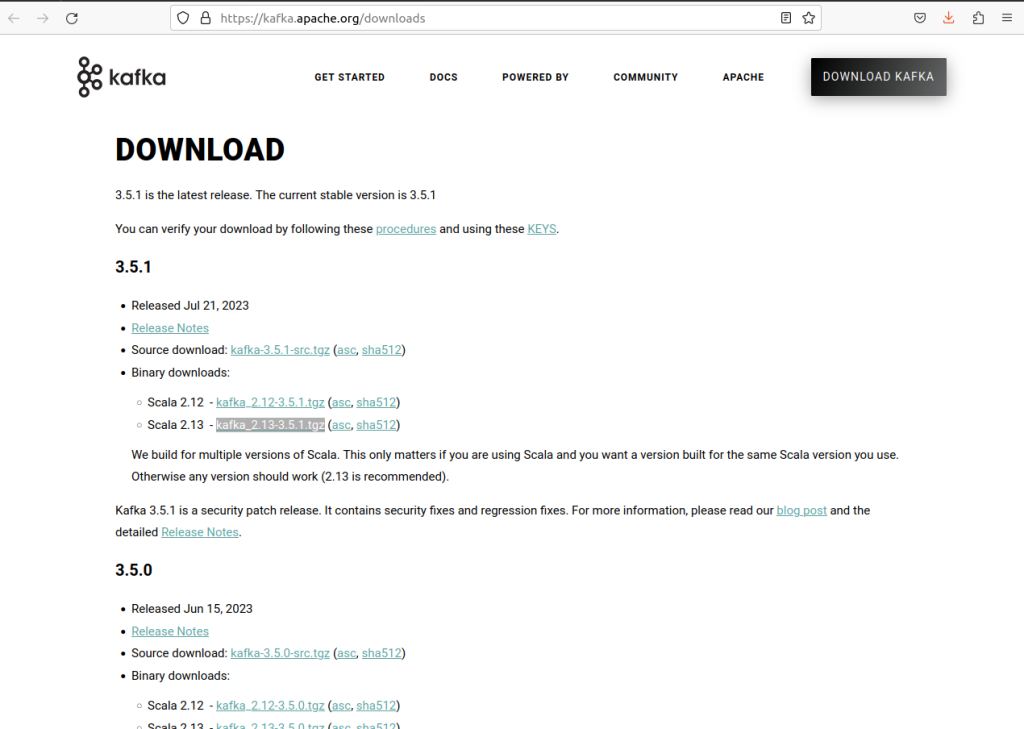
Step 2: On clicking the suitable recent release of Kafka, it will navigate you to a new page that contains Mirror Maker, Click on the first link on that website
Step 3: This will install a tar file in your local. Using the command tar -xvf to untar the file or extract the file
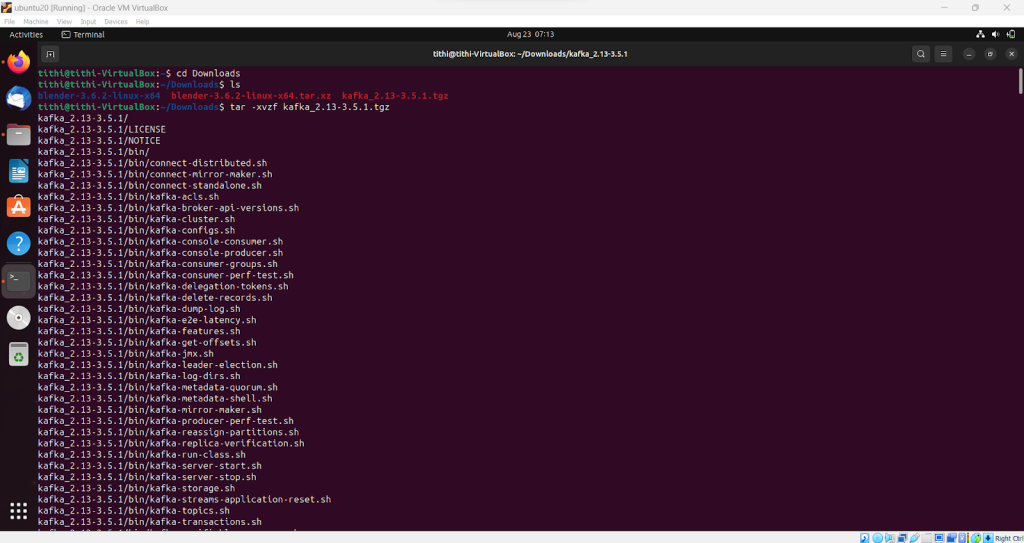
Step 4: Use the ls command to check and verify the installation and extraction are done properly
ls

Step 5: Move to the Kafka downloaded directory by using the cd change directory command
cd kafka_2.12-2.3.0
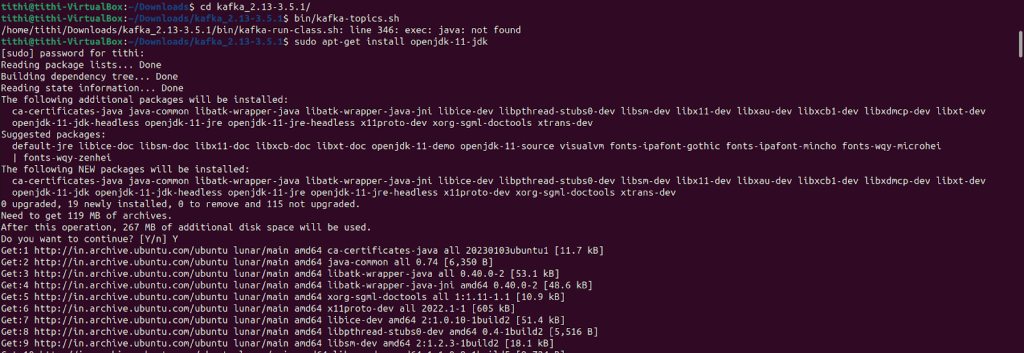
Note: This is the step where you get java not found error, and here if java is not installed you can install as shown in the figure
sudo apt-get install openjdk-11-jdk
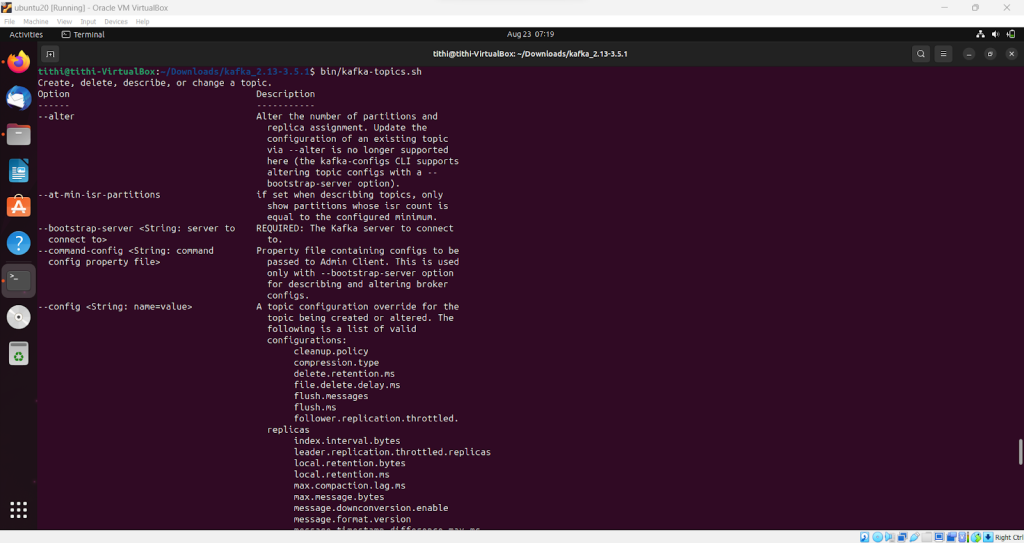
Step 6: Next you have to run the following command and if it runs properly then you are going on the right track
bin/kafka-topics.sh
Step 7: To set the path for Kafka we need to verify that the system contains .bashrc by listing out all files using the following command:
ls -a
Step 8: Open the .bashrc file using the nano or vi editor
Step 9: Move all down the end and set the path for Kafka
export PATH=/home/tute/kafka_2.12-2.3.0/bin:$PATH
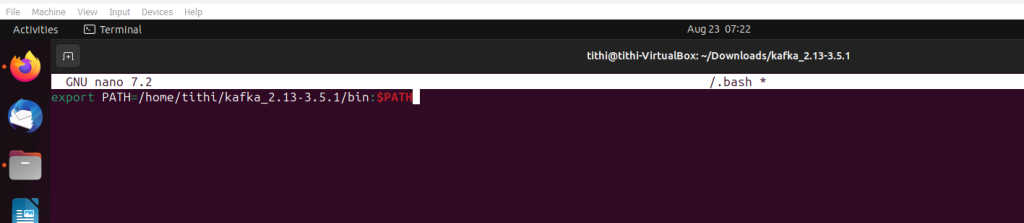
Step 10: Save and exit the editor
Step 11: If the path seems good it will display on the terminal once you close the editor
Step 12: To test the Kafka controls use
kafka-topics.sh
Configuring Kafkactl for Optimal Performance
Step 1: Open the kafkactl script using any editor like nano, vi
nano kafkactl.sh
Step 2: Set up a path to the kafka variable for installation
KAFKA_HOME=/path/to/your/kafka
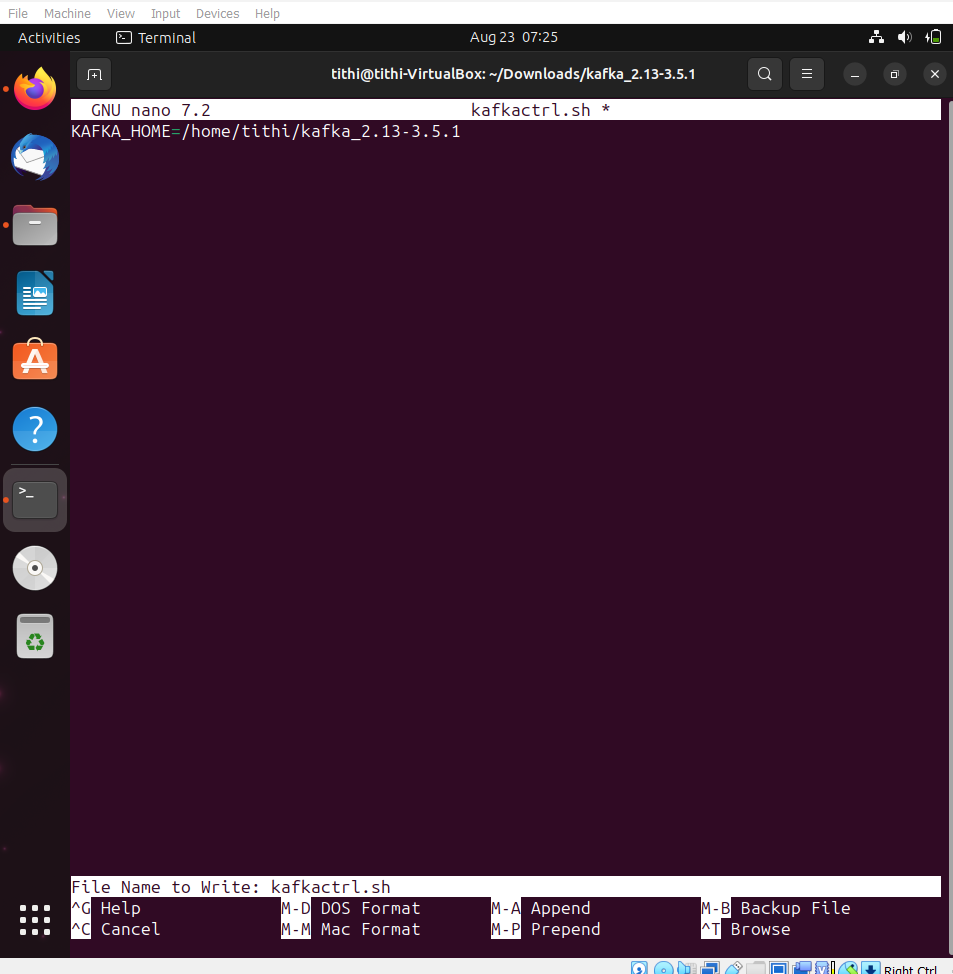
Step 3: Save and exit from the text editor you used to edit
Conclusion
You’ve successfully navigated the intricacies of installing and configuring Kafkactl on your Linux system, elevating your Apache Kafka management skills to a new level. With this newfound expertise, you’re not just managing clusters; you’re orchestrating a symphony of data streams. What challenges will you tackle next in your Kafka journey?
