In this post, we will be learning about the system monitor in Ubuntu Linux. System Monitor is the equivalent to task manager in Ubuntu. System monitor, well, lets you monitor the system. You can have a look at all the processes running, system memory and network usage. System monitor usually comes pre-installed with most versions of Ubuntu. In case you don’t have it installed, you can run the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt install gnome-system-monitor
And to run the system-monitor, you can run the following command:
gnome-system-monitor
You can also press the super key or the Windows key and then type in ‘System Monitor’ and press enter. You will be seeing something like this:
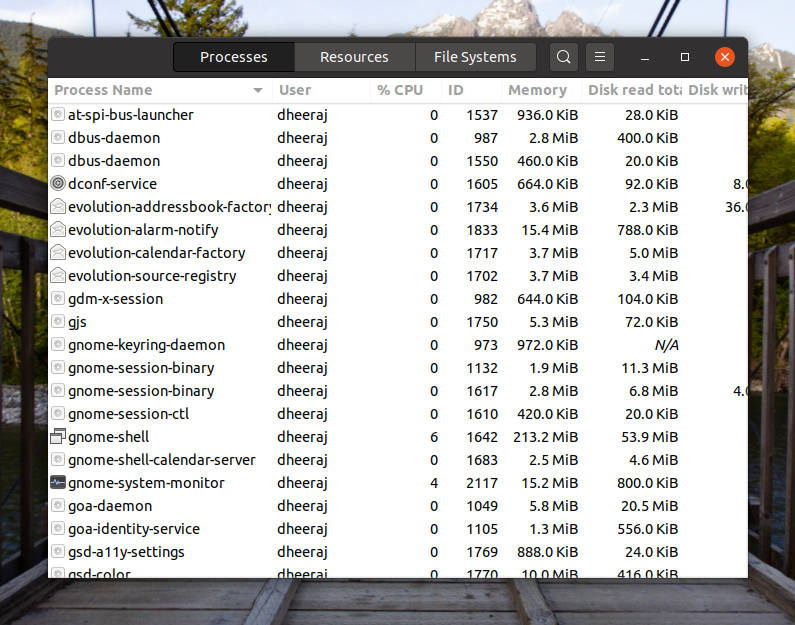
Managing Processes using System Monitor
Managing process is easy with the System Monitor. In the processes tab, you will see a list of all the processes that are running on your machine. While on this window, you can just start typing to search for a processor. You can right-click on any process to manage them.
Here in the background I am running Firefox and will search for the process responsible for running it.
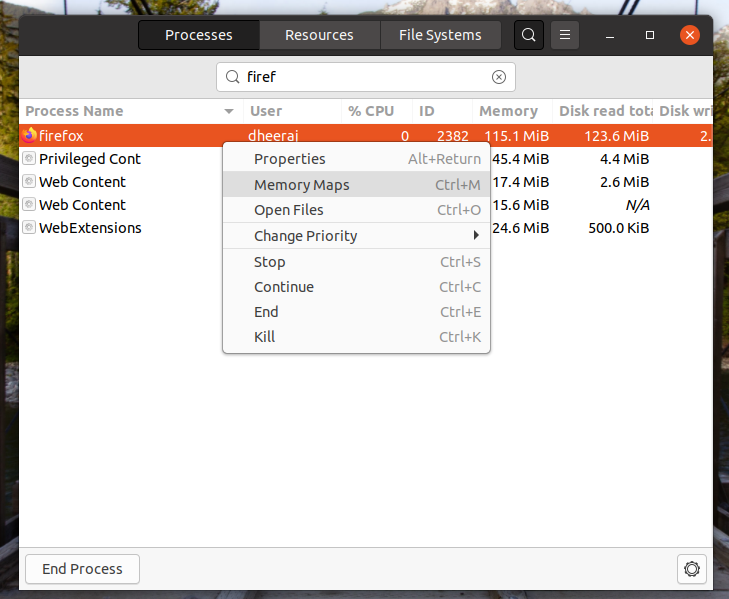
Alright lets first have a look at a processes’ attributes.
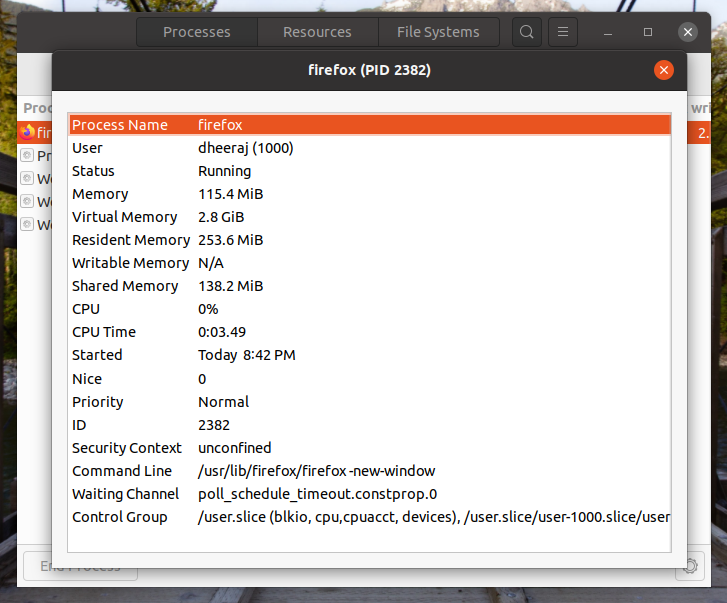
As we can see there are various attributes attached to a process. First, we see the name of the process which is firefox. Then we see the user who is running the process and its status.
After that, we see all the memory details here.
- Memory field shows the main memory that is currently being used by the process.
- Virtual Memory is the area of secondary memory occupied that is being virtually used as the primary memory by the process.
- Resident memory is the memory reserved in the primary memory for the process.
- Shared memory is a piece of memory that is being shared by multiple processes for optimization.
- We also have the CPU usage and CPU running time.
- Nice value decides the priority of the process. By default the priority is 0, it ranges from -20 to 19 with -20 being the highest priority.
- Then we have other details like process starting time, ID, security context, and waiting channel as well.
Monitoring Resources and File Systems
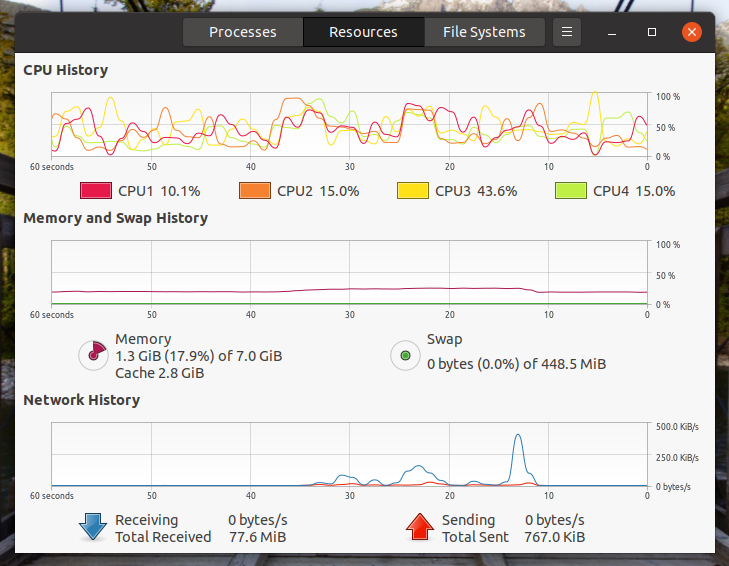
Resource tab has three graphs showing usage of Memory, CPU and Network. It gives you a nice picture of the system on a single window. Most probably if something is wrong with the machine, it will show it’s sign here.
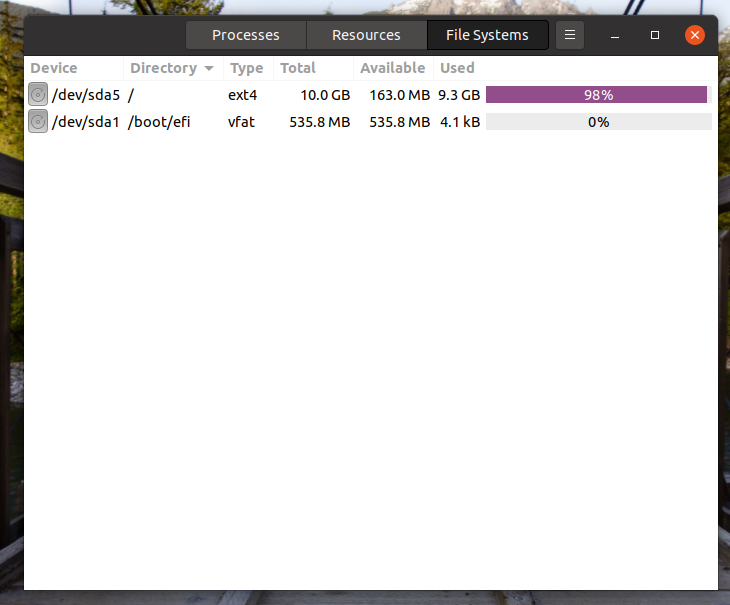
File Systems tab shows all the mounted drives in the system and all essential details attached to it. It will be looking something like this.
Alternatives
System Monitor tools provide a nice GUI experience and provide most of the system details. However, there are other monitoring tools that let you do much more as compared to the System Monitor. I have listed a few of them here, please do check them out:
- htop – A guide to the htop command in Linux
- top- How to Use The Linux top Command
- df – How To Use The df Command in Linux?
- tcpdump – A tutorial on the tcpdump command in Linux
Conclusion
We learned about the system monitor in Linux. I hope this tutorial was helpful and you learned more about monitoring system. Have a great day ahead! Cheers!





