The kill command in Linux is used to send a signal to a process or a group of processes. The name, unfortunately, chosen as kill, instead of signal, does not need to necessarily kill a process. As we will see, based on the values passed to it, it sends an appropriate signal to the Process / Process group.
1. Linux kill Command Basic Syntax
It is a C function, which is implemented in the #include <signal.h> header file in POSIX systems.
The original function takes the form of kill(pid_t pid, int signal), where pid is the Process ID of the process (Group ID of a group of Processes), and signal is the type of signal to be passed.
The Linux command is very similar, and takes the format:
root@ubuntu:~# kill -SIGNAL PID
2. Find the PID of a process
To get the PID of a target process, use the ps command to find the corresponding PID for a process name.
root@Ubuntu:~# ps
To find the list of all user processes (including daemons, backgrounded processes), use:
root@Ubuntu:~# ps aux
3. kill Command – List All Signals
To know the list of all possible signals that kill can send, use the -l (List) option.
root@ubuntu:~# kill -l
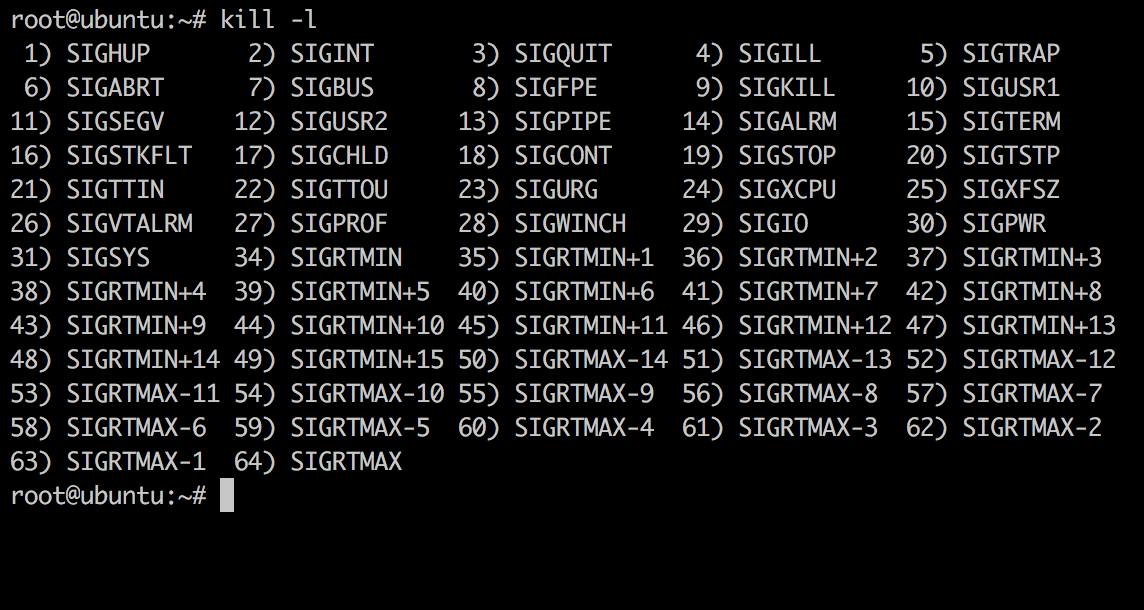
In my system, there are 64 possible choices for signals to kill. The function of each signal can be referred to from the manual page of signal. (man signal)
Here, further examples demonstrate the kill command using common signals like SIGINT (Ctrl+C) and SIGKILL (Ctrl+Z).
4. Linux kill Command – Send Signals to Processes
A signal can be passed in multiple formats:
- Using the Signal Number (Positive Integer)
- Using the Signal Name with the
SIGprefix (SIGINTfor theINT(interrupt) signal) - Using the Signal Name without the
SIGprefix (INT,KILL)
We can send signals to a process/process-group using any of the below formats:
kill -SIGNO PID(Ex.kill -5 101sends the Signal Number 5 to the PID101kill -SIGNAME PID(Ex.kill -SIGINT 101sends the Interrupt Signal (Ctrl + C) to the PID101)kill -NAME PID(Ex.kill -kill -300sends the Interrupt Signal (Ctrl + C) to the Process Group300)
NOTE: If the PID value is negative, it means that we are referring to a Process Group and not just a single process. The third example shows this.
If the PID value is -1, this is a special value that sends the signal to every process except kill and init (init is the first process that spawns when the system boots up and is hence the parent process for every other process)
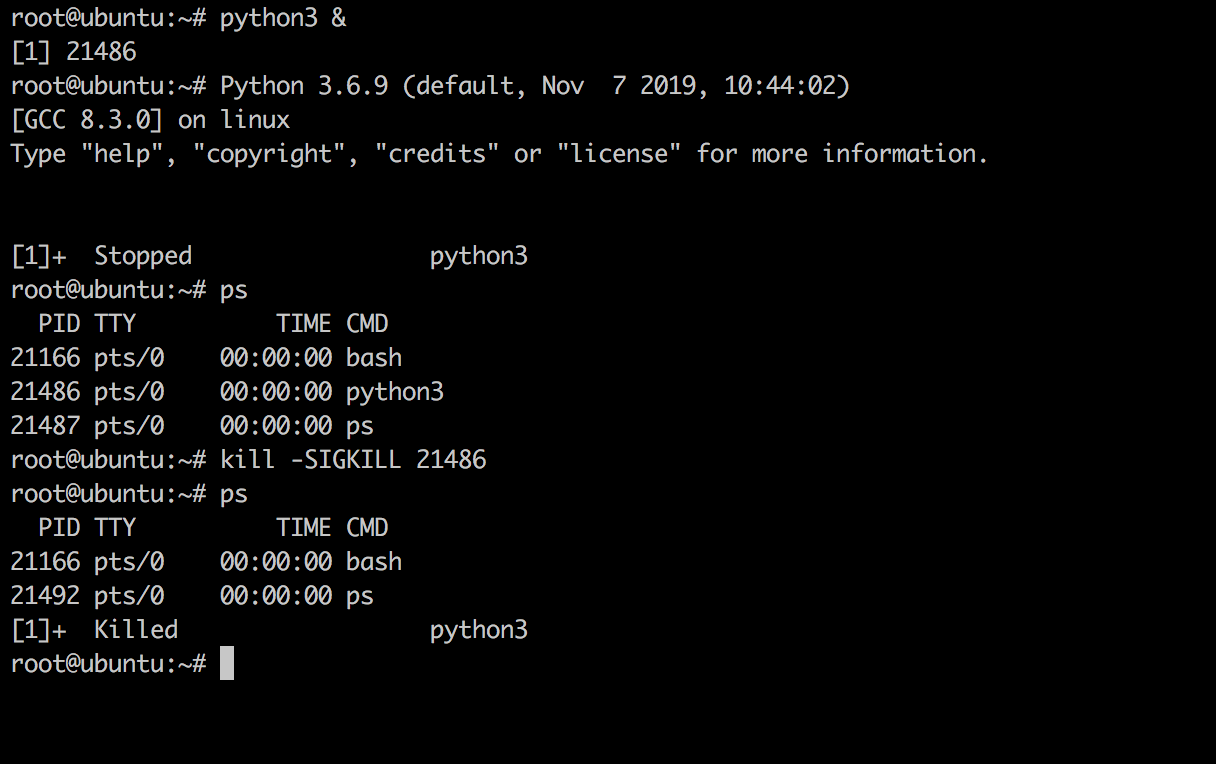
The above example kills a backgrounded process using the kill -SIGKILL PID command. We get the list of all PIDs using the ps command, and then send a signal to kill it.
5. Default signal for kill
kill can also be used without specifying a SIGNAL. This will cause a SIGTERM to be passed as the default signal, which will terminate all matching processes.
Example:
kill 21000
This will terminate the process with PID of 21000.
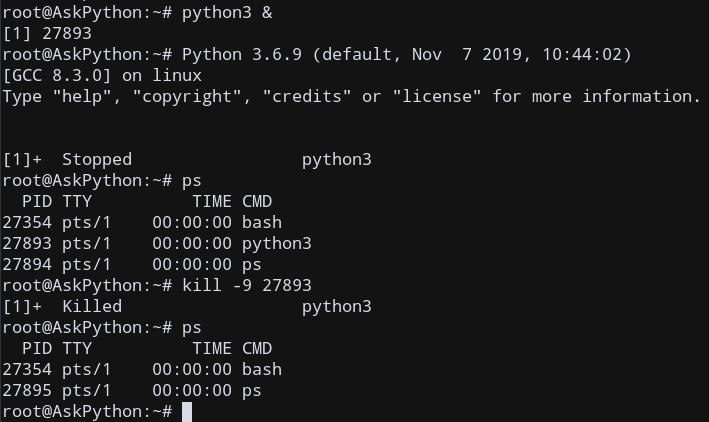
6. kill -9 command
The kill -9 PID command is used to send Signal number 9 (SIGKILL) to PID. This kills the corresponding process.
kill -9 21000
7. Kill a process by name
We cannot directly pass the process name to kill, so there are two ways to achieve this:
7.1) Using killall
Format: killall -SIGNAL NAME
The killall command sends the signal to all processes matching a given name.
killall -9 bash
This sends Signal Number 9 (SIGKILL) to all processes matching the name bash.
killall can also be used without specifying a SIGNAL. This will cause a SIGTERM to be passed as the default signal, which will terminate all matching processes.
Example:
killall vim
7.2) Using pgrep
We can use the pgrep command to output the matching PIDs of a given process name from the user process table.
pgrep bash
Output:
root@HowLinux:~# pgrep bash
26513
26944
27354
pgrep searches for process names from the complete list of processes for a given user.
You can pass the list of PIDs after using pgrep to kill.
pgrep vim | xargs kill -SIGINT
This will kill all user processes called vim (by passing SIGINT to all of them)
If you want to match only the first process id, then use a limited match grep(the -m option).
root@AskPython:~# pgrep bash | grep -m1 ''
26513
Similarly, if you want to match the first two, use:
root@AskPython:~# pgrep bash | grep -m2 ''
26513
26944
8. kill vs killall Command
killis used to send a signal to a Process ID/Group ID, whilekillallis used to send a signal to a list of processes matching a given name.killallsends the signal to possibly multiple processes, whilekillsends the signal to only a single process/process-group.
9. Kill all processes of a user
We can kill all processes that belong to a user using killall, with the -u / (--user) option.
root@Ubuntu:~# killall --user USERNAME
This will kill all processes of the user called USERNAME.
10. Other commonly used kill Signals
| Signal Name | Signal Value | Function |
SIGHUP | 1 | Hangup |
SIGINT | 2 | Keyboard Interrupt |
SIGKILL | 9 | Kill Process(s) |
SIGTERM | 15 | Terminate Process(s) |
SIGSTOP | 17, 19, 23 | Stop the Process(s) |
11. Conclusion
In this article, we learned about the kill command, which is used to send various types of signals to processes and process groups. This is a quick and easy way for programmers to terminate and suspend programs from the Command Line, so if you are not familiar with this command, make sure to do so, as it is a very handy command-line tool. Hope you found this article useful!




