This tutorial will briefly cover the exact steps to install docker on Debian. Docker is a service that runs software in virtually isolated containers. Containers are a standardized unit of software that allows developers to isolate their apps from their environment. This increases the portability of the code and reduces the challenges developers face while collaborating.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to install Docker on Debian 10. Let’s go over it step by step.
Requirements:
- 64-bit version.
- Architectures supported : x86_64 (or amd64), armhf, and arm64
Steps to Install Docker on Debian
Now that we have the requirements in place, let’s get to installing the latest version of docker on Debian from the official docker repository.
1. Update APT and Download Dependencies
The first step is to use the apt command to update the repositories so we can get the latest packages and dependencies:
$ sudo apt-get update
This will update the package index. Next, we need to install prerequisite packages to let apt use packages over HTTPS.
$ sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg2 software-properties-common
2. Add Docker Repositories to Debian APT Sources
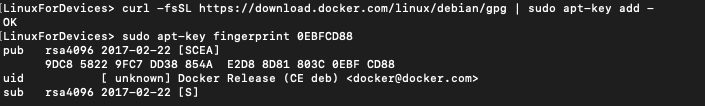
Next, we will add the docker repository GPG key to our apt keys using the following command:
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
We will run the apt-key fingerprint command to confirm the correct fingerprint. The following is the fingerprint for the latest docker version on their official website:
$ sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
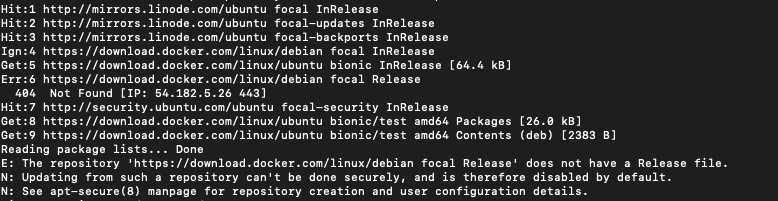
Finally, let’s add the repository to our Debian database to ensure that we can download the packages from the repo:
$ sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
The lsb_release -cs sub-command returns the name of your Debian distribution.
3. Installing Docker Engine
Let’s update the apt repositories again so we can get the packages from the docker repo that we just added.
$ sudo apt-get update
Once we are done with all the steps above, we can finally go ahead and install Docker. For that run the command :
$ sudo apt install docker-ce
Press ‘y’ to process the installation.
4. Verify the Installation
To check if the installation was successful, run :
$ docker -v

This means you are all set to go and rock with your docker!
Conclusion
That’s about it. You now have a complete install of Docker on Debian. If you want to learn more about using Docker to spawn containers, you can view the Docker documentation.
What are the prerequisites for installing Docker on Debian?
Before installing Docker on Debian, make sure you have a Debian 12 system, updated with the latest packages using ‘apt update’ command.
How can I install Docker on Debian?
To install Docker on Debian, you can run the following command: ‘apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io.
How do I start a Docker container after installation?
You can start a Docker container by running the command ‘docker start CONTAINER_ID’ in your terminal.
What is the command to stop Docker from running?
To stop Docker from running, you can use the command ‘systemctl stop docker’ in your terminal.
What are some common Docker commands that I should know?
Some common Docker commands include ‘docker run’, ‘docker ps’, ‘docker stop’, ‘docker rm’, and ‘docker images’.
How do I manage Docker containers and images?
You can manage Docker containers and images using commands like ‘docker ps’, ‘docker images’, ‘docker pull’, ‘docker stop’, and ‘docker rm’.
What is Docker containerization and how does it relate to Docker?
Docker containerization is a method of packaging, distributing, and running applications within containers. Docker uses containerization to isolate applications and their dependencies, making it easier to deploy and manage applications across different environments.
What are Docker packages?
Docker packages are software packages that contain all the necessary files and instructions to install Docker on a system.
