Hello guys, In this article, We will discuss how to backup single and multiple MySQL databases. We can backup MySQL databases using mysqldump utility. The backup files created by mysqldump consists of SQL statements that can be used to recreate the original databases.
It can also be used to backup and restore the database on a remote server at the same time or transfer the database to another server. You should backup your databases daily or you may lose all the data if a hard-drive failure or bug occurs.
Mysqldump command
The basic syntax of mysqldump command is as follows:
mysqldump [options] > filename
Backup a single MySQL database
To back up a single database, first, create a backup of the database by logging in as root by executing the following command.
mysqldump -u root -p databasename > filename
Enter your MySQL root user password if prompted. Save it to a file named backup.sql.
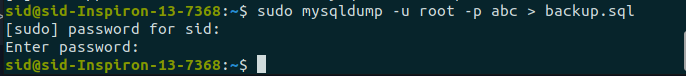
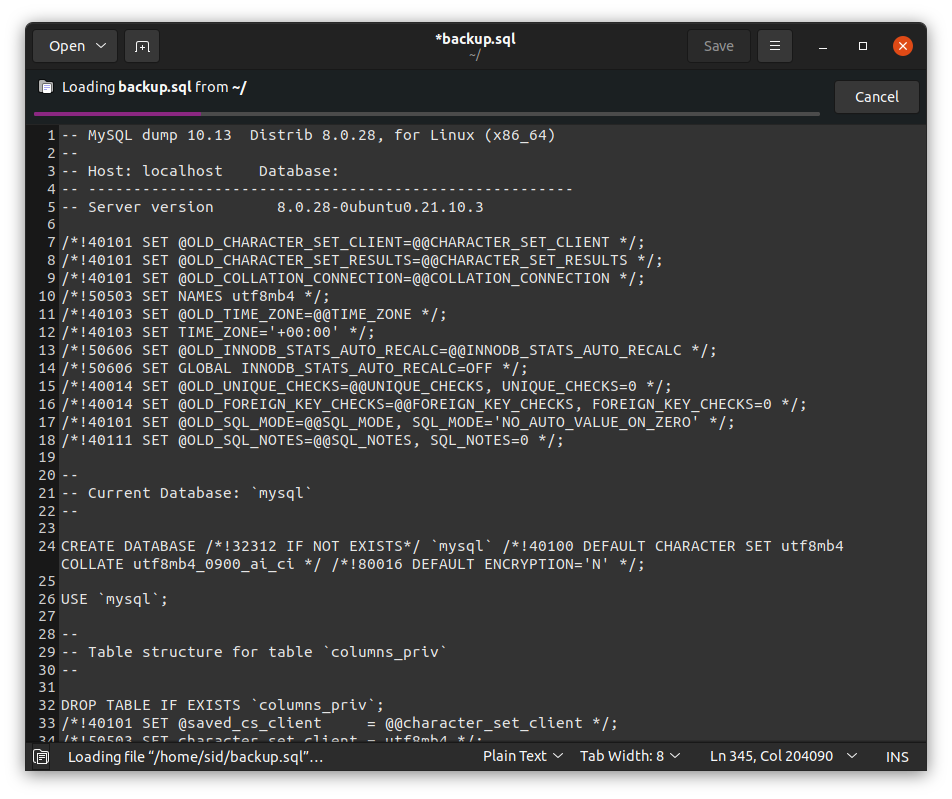
mysqldump -u root -p abc > backup.sql
If you are already logged in as root, change the above command as shown:
mysqldump databasename > filename
Backup Multiple MySQL Databases
To back up multiple MySQL databases, use –databases to list multiple databases as shown:
mysqldump -u root -p --databases databasename1 databasename2 databasename3 > filename
mysqldump -u root -p abc1 abc2 abc3 > backup.sql

Backup All MySQL Databases
To back up all the MySQL databases, simply replace –databases to –all-databases in the above command, as shown:
mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > backup.sql

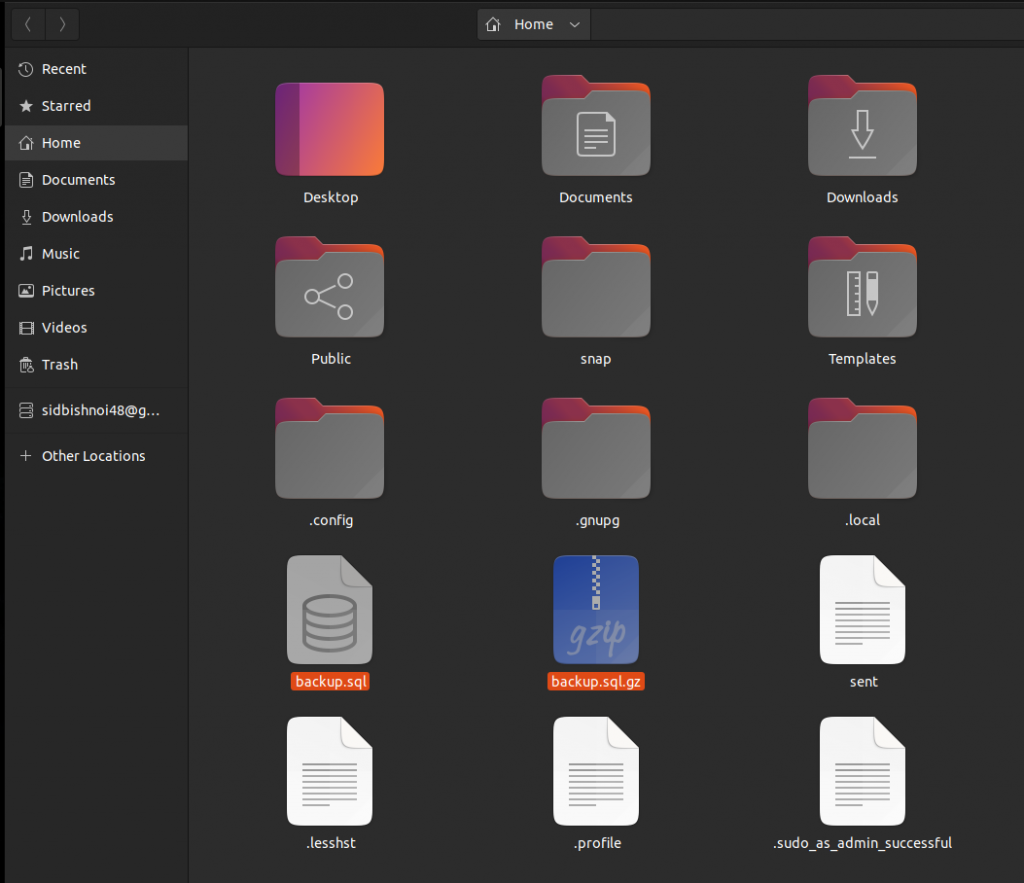
Backup MySQL Database in a Compressed File
Sometimes, the databases may be too large in size, we can also back up the databases to a compressed file using the gzip utility, as shown:
mysqldump databasename | gzip > filename.sql.gz

Restore the Backup File
To restore the backup file, You can do it by running a command as shown:
mysql databasename < filename.sql
mysql abc < backup.sql

Conclusion
So, We learned how to single, multiple, and all databases using a single line command. We also covered backing up the databases to a compressed file and restoring the backup file. Thank you for reading!