Secure Boot is a UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) firmware security feature created by the UEFI Consortium that ensures your computer boots up securely and safely by preventing unauthorized software from taking over your system. It boots only those bootloaders that are signed in to the UEFI firmware.
A secure boot is sort of a security gate. It analyzes code before you execute it on your system. It permits code to run if it has a valid digital signature and prevents code from running if it is not recognized.
Also read: How to Install Arch Linux
While it’s a good upgrade from the legacy BIOS, UEFI secure boot can come in the way of installing Linux distros. In this article, let’s look at how we can disable secure boot to install Linux. Once installed, you can re-enable UEFI and your existing Linux install will be unaffected.
Accessing the UEFI boot menu
The secure boot protects your system from malware variants like rootkits and boot kits. It is not advised to turn it off, until it is required. In this case, you need to disable it if you want to dual-boot with Linux.
The first step involves accessing the UEFI menu. You can do it in 2 ways, i.e.
- by pressing a specific function key while your PC is booting, such as F1, F2, F12, or Esc.
- Using the Windows menu.
Steps to disable Secure Boot from the Windows menu
Step 1: Search for UEFI -> Go to Change advanced startup options.
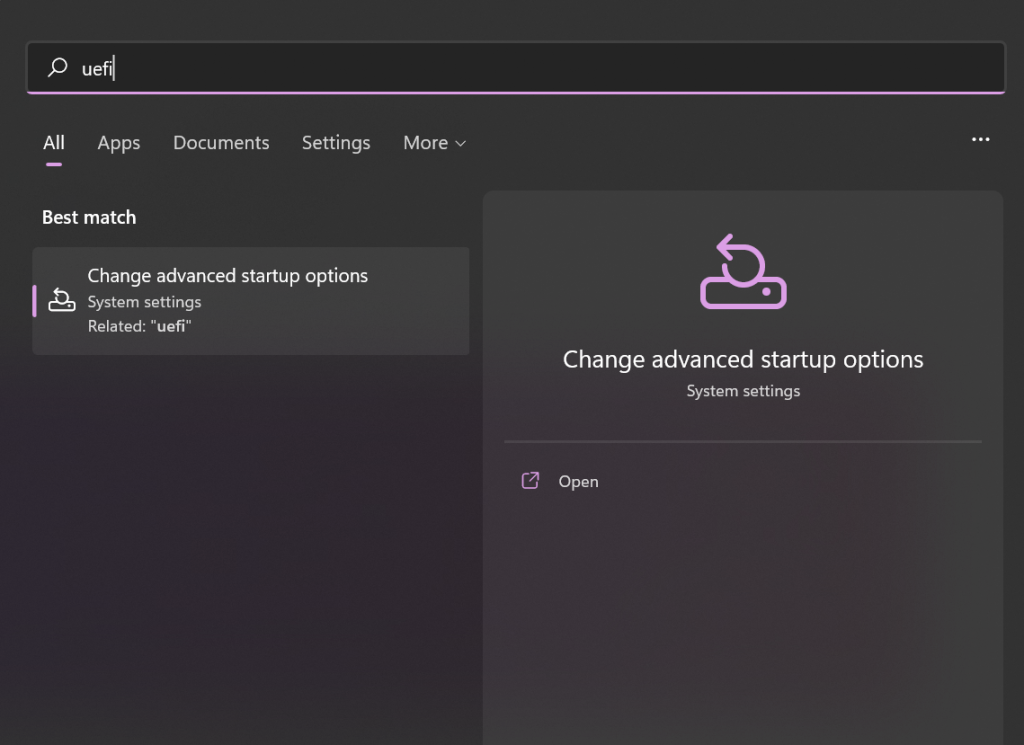
Step 2: Now, click on Restart Now under the Advanced startup option.
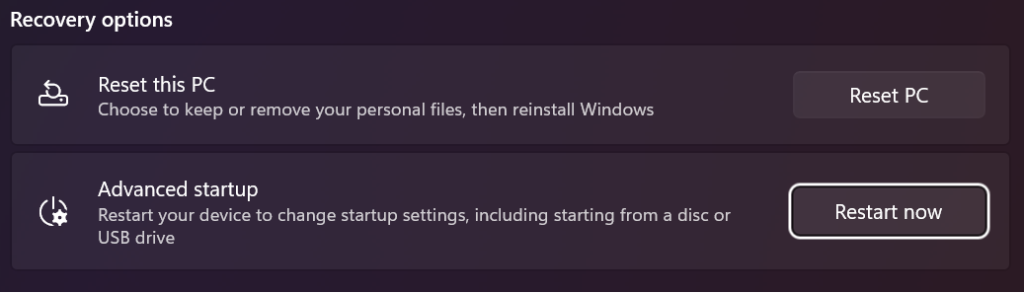
Confirm that you want to restart your computer and let Windows automatically restart to advanced startup.
Step 3: After that select the Troubleshoot option on the next screen that appears.
Step 4: While other systems might prompt you to select advanced options, some will display the UEFI setting option. If you see the UEFI setting option, click on it. Alternatively, pick advanced.
It will notify you to restart in order to change any UEFI firmware settings. When you click the restart button, the BIOS/UEFI settings interface will appear.
Disabling secure boot in UEFI
Once you enter the UEFI utility, you’ll be able to change various settings here, including disabling secure boot. To disable secure boot, follow the following steps:
Step 1: Navigate to the Boot tab in the UEFI/BIOS configuration. The secure boot option can be found here and is currently enabled.
Step 2: Go to the Secure Boot option now, and then press Enter to choose it. Change its value with + or -, then choose Yes to confirm it.
Now that Secure Boot has been successfully disabled, you can finally explore the operating system of your choice by grabbing the closest previously bootable USB drive.
Conclusion:
Given the prevalence of ransomware today, a secure boot is more important than ever. Secure boot adds an additional layer of system validation to UEFI systems, enhancing system security. It might need to be turned off if you’re trying to install the second operating system because otherwise, you won’t be able to modify your system.
How do I disable Secure Boot on my Dell laptop running Ubuntu?
To disable Secure Boot on your Dell laptop, you need to access the firmware setup. Reboot your machine and hold the appropriate key (usually F2 or DEL) to enter the BIOS setup. From there, navigate to the Secure Boot option and change its state to Disabled.
What must I do if Secure Boot is enabled and I’m trying to install a bootloader?
If Secure Boot is enabled, you must disable it first to install a third-party bootloader, such as GRUB. This is because Secure Boot can prevent unsigned bootloaders from executing, which may lead to problems during installation.
Can I disable Secure Boot without a password?
In most cases, you can disable Secure Boot without a password. However, some systems may require you to enter a firmware password if it has been set. If prompted, you will need to check with your computer’s documentation for guidance on resetting or bypassing the password.
What is the reason for disabling Secure Boot in UEFI systems?
The primary reason for disabling Secure Boot in UEFI systems is to allow the installation of operating systems and applications that are not signed with a recognized key. This is particularly important for users who are installing Linux distributions or custom kernels that may not be compatible with Secure Boot.
Is it safe to disable Secure Boot on my computer?
Disabling Secure Boot can expose your computer to certain risks, as it allows unsigned code to run. However, if you are installing a trusted operating system like Ubuntu and follow secure practices, it can be done safely. Just ensure that you are aware of the implications and keep your system updated.
How can I check if Secure Boot is currently enabled on my system?
You can check the status of Secure Boot by entering the BIOS setup during boot. Look for a section labeled Secure Boot in the firmware settings. On some Linux systems, you can also check the Secure Boot state using the command `mokutil –sb-state` in the terminal.
What happens if I try to boot Linux with Secure Boot enabled?
If you try to boot Linux with Secure Boot enabled and the OS or bootloader does not have a valid signature, you will likely encounter a boot error or the system may not boot at all. Disabling Secure Boot is often necessary for a smooth installation and booting experience.
Do I need to reinstall my OS after disabling Secure Boot?
No, you do not need to reinstall your OS after disabling Secure Boot. However, if you encounter any boot issues, you may need to reinstall or repair your bootloader, especially if it was not configured to work with Secure Boot initially.
Can I dual-boot Windows 8 and Ubuntu with Secure Boot enabled?
Yes, you can dual-boot Windows 8 and Ubuntu with Secure Boot enabled, but it may require specific configurations. Make sure that your Ubuntu installation media is signed and that your firmware settings allow for compatible operating systems. If you face issues, consider disabling Secure Boot.
Which method is the fastest to disable Secure Boot in UEFI?
The fastest method to disable Secure Boot is to boot into your firmware setup, usually by pressing a specific key during startup (like F2 or DEL). Once in the setup, navigate to the Secure Boot settings and switch it to Disabled. This method typically takes only a few minutes.
