Let’s talk about the different ways to exit vim editor here. As you would know Vim is a Linux utility for editing text. The special aspect of only using the keyboard to edit makes it a unique editor. With this aspect comes a difficulty that you can not exit the editor by clicking on the ‘cross’ button. There is no pop-up window, which confirms your decision of quitting. That is the main reason, thousands of computer experts sometimes stumble upon the problem of “how do I exit Vim?”.

Let’s see the 10 different ways to exit vim editor
1. Simply Exit Vim
After editing the text and saving your progress, you simply type :q or :quit in the editor. As soon as you press ':', outside the insert mode, you will notice the commands appearing on the bottom of the screen.
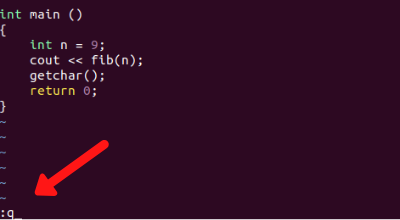
Note: In case you can not see the command
:qat the bottom of the screen, that means you are still inside the insert mode. To exit the insert mode, pressESC(escape) key.
However, it may happen that you forget to save what you edited or you edited but do not wish to save. Vim is unable to make such differences and confirms your decision of quitting. This task of reassurance is shown by an error on the bottom of the screen.
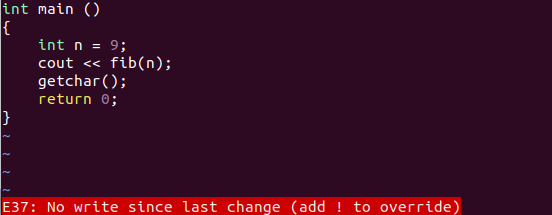
The error E37 means that you have not saved (write) after the last change. In order to quit no matter what, you have to override the quitting command by using the exclamation mark.
2. Force Quit Vim
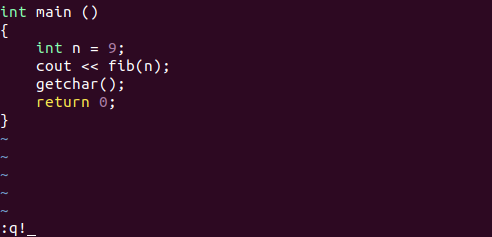
If you desire to discard any changes done to the text and just exit the Vim editor, then Vim has a forced quit command :q!
3. Confirm and Quit
Similar to the error mentioned above, E37, Vim provides a confirmation in case you wish to quit after making some changes to the text. To make use of this confirmation, type :conf q and press ENTER.
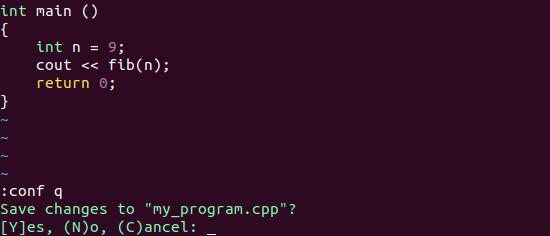
You will press the key S if you wish to save the changes, otherwise press N. To prevent the editor from closing, you can enter C.
Note: This confirmation message only appears if there have been some changes made to the existing file, otherwise it will close automatically.
4. Save and Exit Vim editor
After making some progress in the buffer, you now wish to save all the changes and continue on your next venture. In order to save and quit in one single command, Vim has :wq.
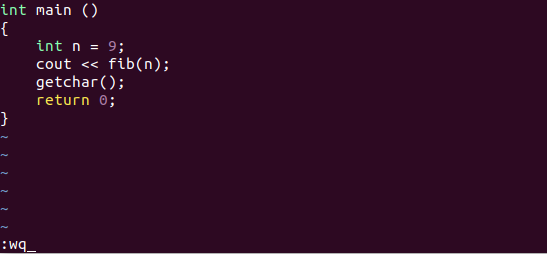
This command initially does a disc write (:w), and follows with the simple quit (:q).
5. Save (if necessary) and Quit
To save the system from unnecessary disc write, Vim has a feature of saving ‘only if’ the text was altered. To make use of this feature, the command is :x.
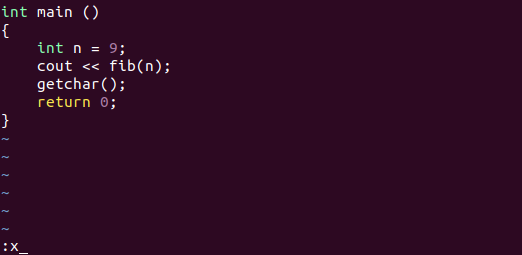
6. Save (if necessary) and Quit (Alternative)
As an alternative to :x for performing necessary save and quit, Vim has a cool way to quit that does not even require the ENTER key. Pressing SHIFT + ZZ will do the same job. After pressing it the first time, you can see Z on the bottom of the screen and as soon as you press it the second time, Vim is already closed.

SHIFT + Z 7. Force Quit (Alternative)
Instead of using :q! to force quit from Vim editor, you can take advantage of another force quit method, by pressing SHIFT + ZQ. Similar to the previous technique, after feeding in SHIFT + Z, you will see Z on the bottom right of the editor. Just as you press SHIFT + Q, the editor will close automatically, no matter your progress.
8. Quit All
When your day’s job is finished and you want to quit all the files at once, you can do so by the command :qa or :qall. It exits from all the saved files at once and may stop at those which have unsaved changes. In order to, force quit all of them, :qa! or :qall! comes in handy.
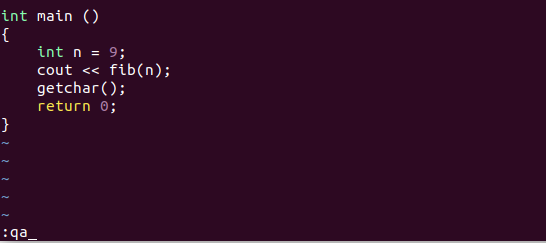
9. Quit All with Error Code
Similar to :qa!, the command :cq or :cquit exits from all files, but with a slight difference. When it exits, it sends out an error code. The system understands the type of exit from the error code and stops the file from being compiled. Since there has been no saving, all the changes are lost.
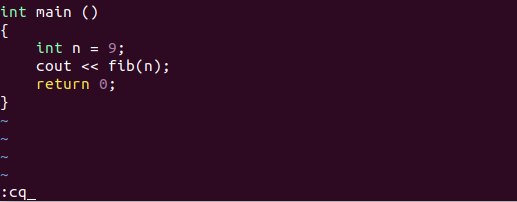
10. Save and Quit All
After finishing your project if you wish to close all your programs and save them all, then you can enter the command :wqa or :wqall. This command will write all the buffers and exit.
References
Vim documentation : editing – For more variations on writing and quitting files using Vim.
What is the basic way to exit the vi editor in Linux?
To exit the vi editor, you can return to command mode by pressing the ESC key and then typing `To save your filename and quit, type :wq in command mode.` to save changes and quit.
How do I exit vim without saving changes?
To exit vim without saving any changes, press the ESC key to enter command mode, then type `:q! is a common command in vi or vim.` and hit Enter.
Can you explain how to open a file in the vi editor?
To open a file in the vi editor, you can use the command line by typing `vi filename` in your terminal, where ‘filename’ is the name of the file you want to edit.
What is the difference between the vi and vim text editors?
The vi editor is the original text editor created for Unix in 1976, while vim (Vi IMproved) is an enhanced version introduced in 1996 that includes additional features and improvements.
How do I create a How do I create a new file in vi?new file in vi?
To create a new file in vi, simply type `vi newfile` in your terminal. This will open a new file called ‘newfile’ in the vi editor.
What should I do if I opened a file in read-only mode?
If you open a file in read-only mode, you can either exit using `:q` or `:q!`, or if you want to make changes, use `:wq!` to save and exit, but be aware that you may need to adjust file permissions.
How can I navigate within a file in the vi editor?
You can navigate within a file in the vi editor using the arrow keys, or by using the h (left), j (down), k (up), and l (right) keys while in command mode.
What does the colon (`:`) do in the vi editor?
The colon (`:`) in the vi editor is used to enter command mode from input mode, allowing you to perform various commands like saving, quitting, or searching.





