This article demonstrates the various ways to find the Linux version of your system. Linux version can either mean the kernel version that runs the entire system or the version of the Linux distribution currently using. If you wish to find out the Linux kernel version, then head here, otherwise proceed with this article.
The version of Linux distribution is required for identifying the proper kind of software that must be installed on a system. The Linux distribution version is synonymous with the OS version, as Linux is a kind of Operating System.
Find the Linux Version
Let us quickly move on to the methods of uncovering the Linux version.
1. Extracting the Linux version from the os-release file
The /etc/ directory contains a whole lot of information related to the system. It includes the details regarding the OS version. In order to fetch the Linux version, we will extract the os-release file.
cat /etc/os-release
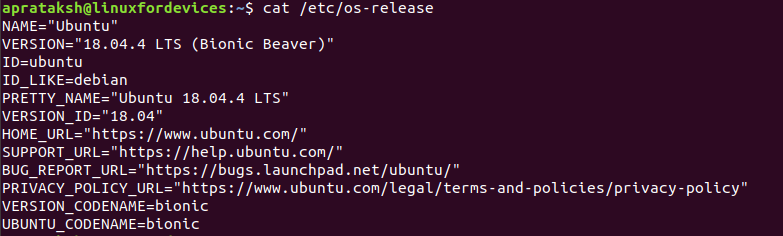
The cat command is responsible for displaying the entire contents of a file in Linux. The above output indicates that the Linux version of the system is “Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS”.
There are few other details like the code name for the Ubuntu version – “Bionic Beaver” and the Linux distribution on which Ubuntu is based (ID_LIKE) – “Debian”.
2. hostnamectl command
An abbreviation for “Control the system hostname”, the hostnamectl command is a Linux tool for modifying and fetching details related to the host system. In order to extract the version of the Operating System, we can use the grep command.
hostnamectl | grep "Operating"

As seen in the above figure, the version of the Linux distribution is identical to the one in the previous method, that is, “Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS”. LTS stands for “Long-Term Support”. Refer the man pages for more information using man hostnamectl command.
3. lsb_release command
The Linux Standard Base (LSB) is a combined project issued by many Linux distributions to generalize methods of achieving tasks in different types of Linux. In order to fetch the version of Linux distribution, we run:
lsb_release -a
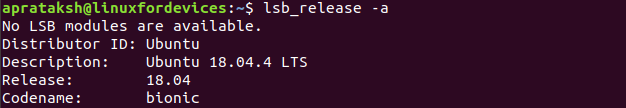
No surprises in the output of the command, as it is bound to match which the outputs of other commands. In order to learn more about the lsb_release command, we can access the manual pages by running man lsb_release.
4. Extracting the Linux version from the /etc/issue file
The issue file is a system identification text file. Using the cat command, we can access its content through the terminal.
cat /etc/issue

It may contain certain character sequences as it used to display the message before the login prompt. Here \n prints the host name, whereas \l prints the current tty line.
Conclusion
None of the methods in this article is complex for any class of Linux user. The filenames like os-release and issue are consistent in all the Linux distributions, so they may not pose any problem.
We hope this article was up to reader’s expectations. Feel free to comment below for any queries.
