Keeping Ubuntu up to date is important for two main reasons: security and software stability. Security updates fix vulnerabilities in the operating system that could be exploited by malicious software or attackers. Software updates improve the stability of the system by fixing bugs and improving performance.
Application Management Best Practices
It is important to follow best practices for application management to ensure that the system is secure and stable.
Some best practices for application management include:
- Installing applications from trusted sources: Applications should be installed from trusted sources, such as the Ubuntu Software Center, to ensure that they are safe and free of malware.
- Keeping applications up to date: Applications should be kept up to date to ensure that they are secure and have the latest features.
- Uninstalling unnecessary applications: Unnecessary applications should be uninstalled to free up disk space and reduce the attack surface of the system.
Keeping Ubuntu Up To Date
There are two ways to keep Ubuntu up to date: via the command line or using the graphical user interface (GUI). The command line is the preferred method for experienced users and system administrators. The GUI is the preferred method for casual users.
To keep Ubuntu up to date via the command line, use the apt update and apt upgrade commands. To keep Ubuntu up to date using the GUI, use the Software Updater application.
Via Command Line
The quickest and easiest way to keep Ubuntu up to date is via the command line. To do this, open a terminal and type the following commands:
- sudo apt update
- sudo apt upgrade
Using apt update
The apt update command will update the list of available packages and their versions. This is useful if you want to see what packages are available for an upgrade before you actually upgrade them.
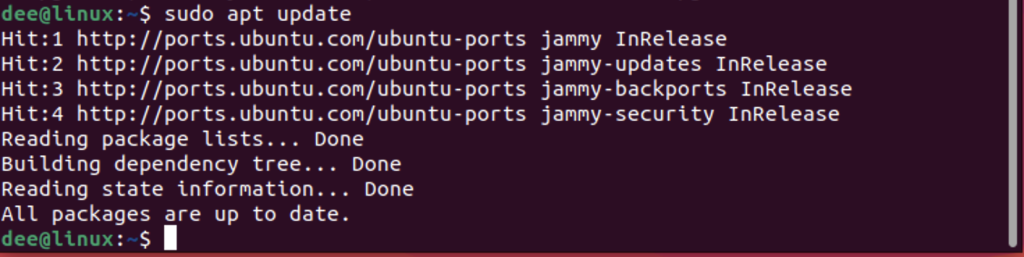
To use apt update, open a terminal and type the following command:
sudo apt update
Using apt upgrade
The apt upgrade command will upgrade the packages to their latest versions. This is useful if you want to upgrade the packages as soon as new versions are available.
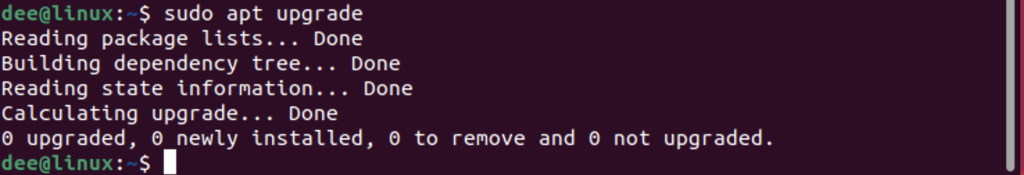
To use apt upgrade, open a terminal and type the following command:
sudo apt upgrade
Update Commands Can Also Be Combined
The update process can be combined into a single command by using the apt-get command. This command will update the list of available packages and their versions, and then upgrade the packages to their latest versions.
To use the apt command, open a terminal and type the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
List Packages Scheduled for the Update
To see which packages are scheduled for the update, use the apt list --upgradeable command. The command lists all packages that have a newer version available. The output includes the current and new versions of the package.
While the sudo apt update command only refreshes the package cache, it does not make the list of the available updates. The --upgradable command, unlike the upgrade command, does not download or install the packages.
To use the command, open a terminal and type the following command:
apt list --upgradeable

Clean up After Update
After the update is complete, it is important to clean up the system. This can be done by using the apt-get command with the clean and autoremove options.
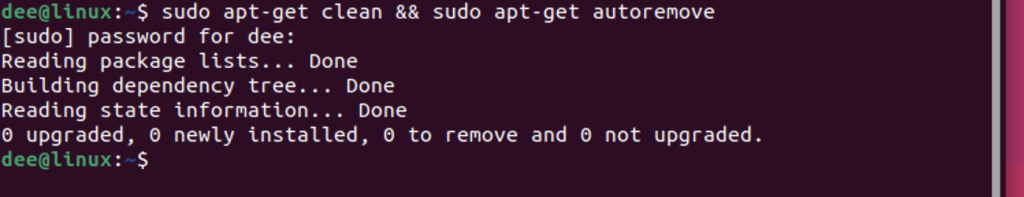
To use the apt-get command, open a terminal and type the following command:
sudo apt-get clean && sudo apt-get autoremove
Configuring Unattended Upgrades
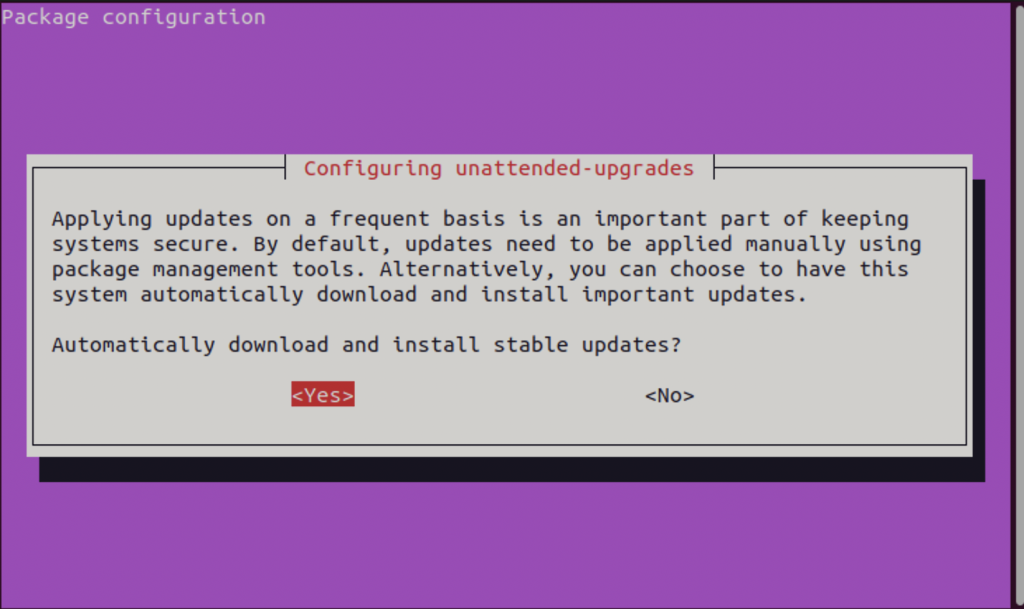
Unattended upgrades are a feature of Ubuntu that allow the system to install security updates automatically. This is useful for servers that need to be kept up to date without manual intervention.
To configure unattended upgrades, open the Terminal and type the following command:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure --priority=low unattended-upgrades

Enabling Livepatch to Ensure Server Uptime During Kernel Updates
Livepatch is a feature of Ubuntu that allows the system to patch the kernel without rebooting. This is useful for servers that need to be kept up and running with minimal downtime.
To enable livepatch, open the Terminal and type the following command:
sudo canonical-livepatch enable MACHINE-TOKEN
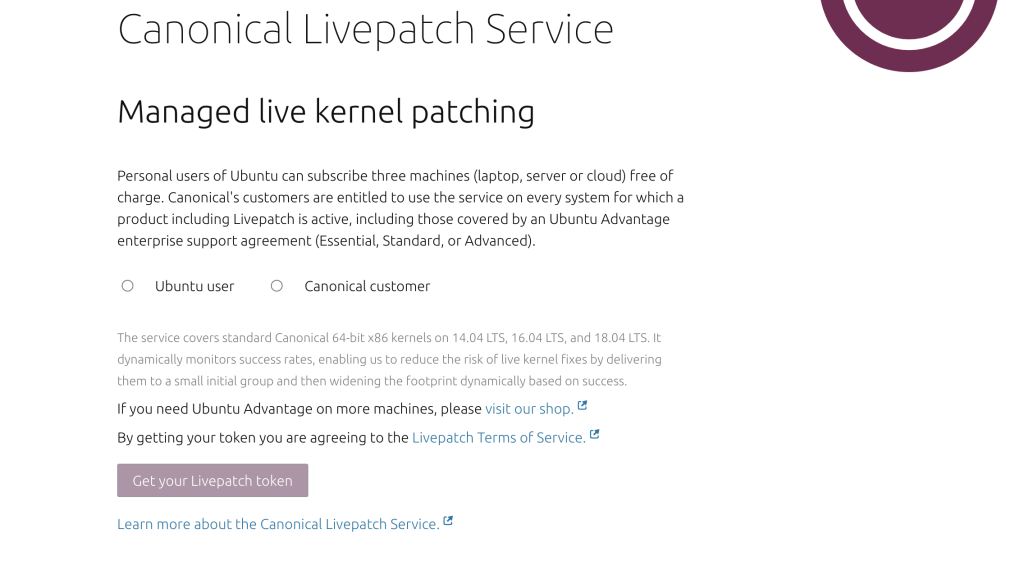
Note – The MACHINE-TOKEN needs to be obtained from the https://auth.livepatch.canonical.com/ website.
Depending on the kind of user, you need to go ahead and select the appropriate option, upon which the site will generate the MACHINE-TOKEN that you can use to then enable the live patch.
Via Graphical User Interface
The quickest and easiest way to keep Ubuntu up to date is via the graphical user interface (GUI).
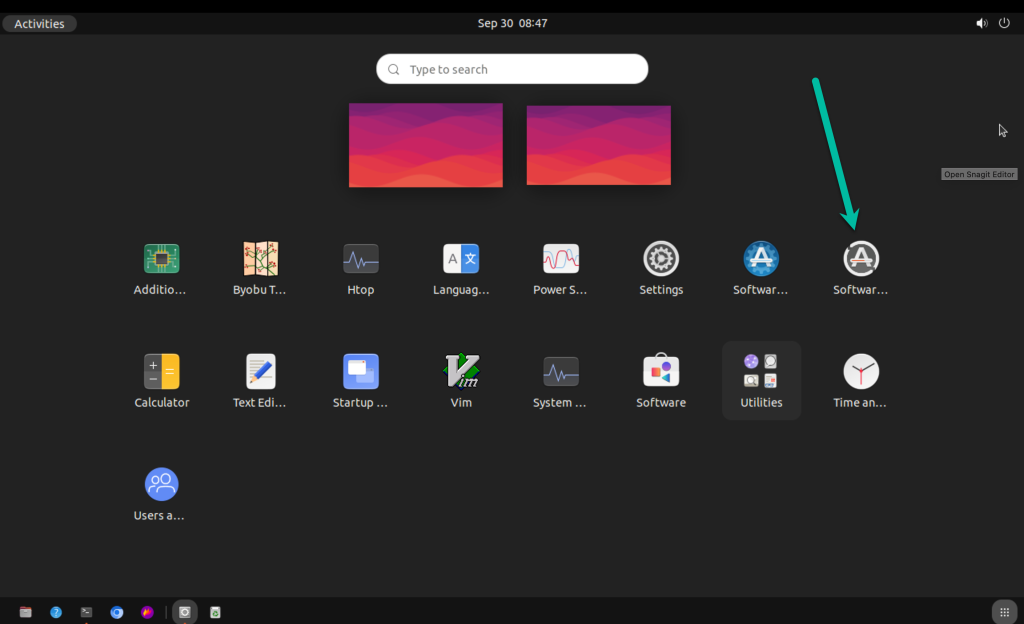
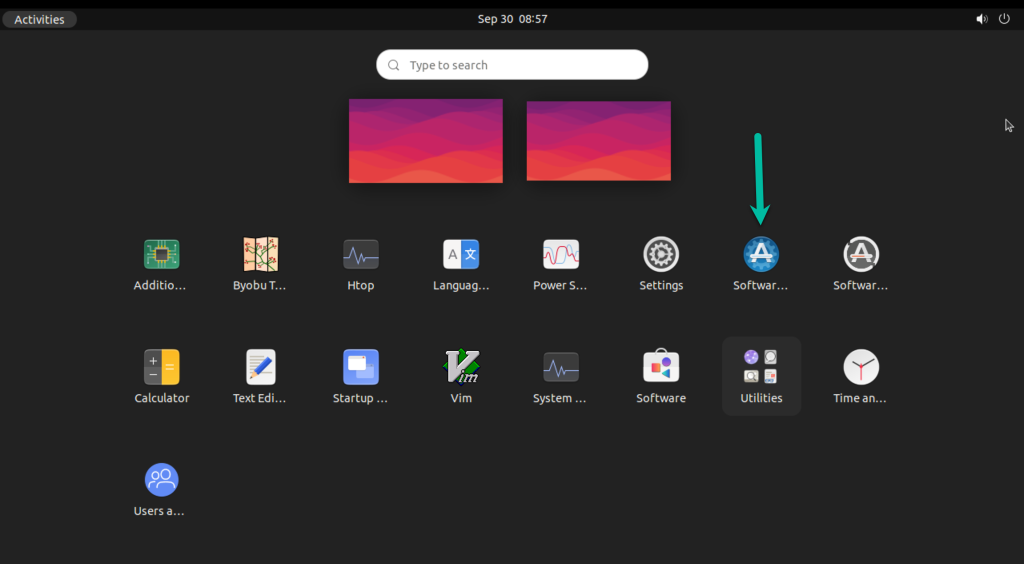
Step 1. Press Show Applications

Step 2. Open the Software Updater application and click the Check for Updates button.
Step 3. The Software Updater will check for available updates and prompt you to install them. To install the updates, click the Install Updates button.
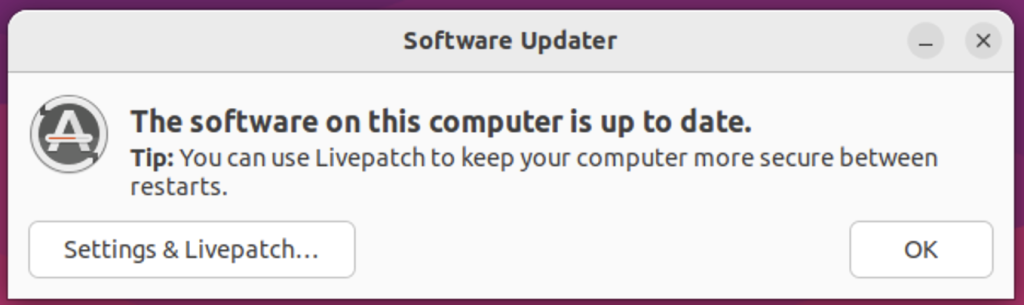
Step 4. If no updates are available for installation or upgradation, you will receive a up-to-date notification like so,
Upgrading to A New Version of Ubuntu
Ubuntu releases a new version of the operating system every six months. These releases include new features and security fixes. Users can upgrade to a new version of Ubuntu manually or automatically.
Upgrading to a new version of Ubuntu is important for two main reasons: security and new features.
There are two ways to upgrade to a new version of Ubuntu: manually or automatically.
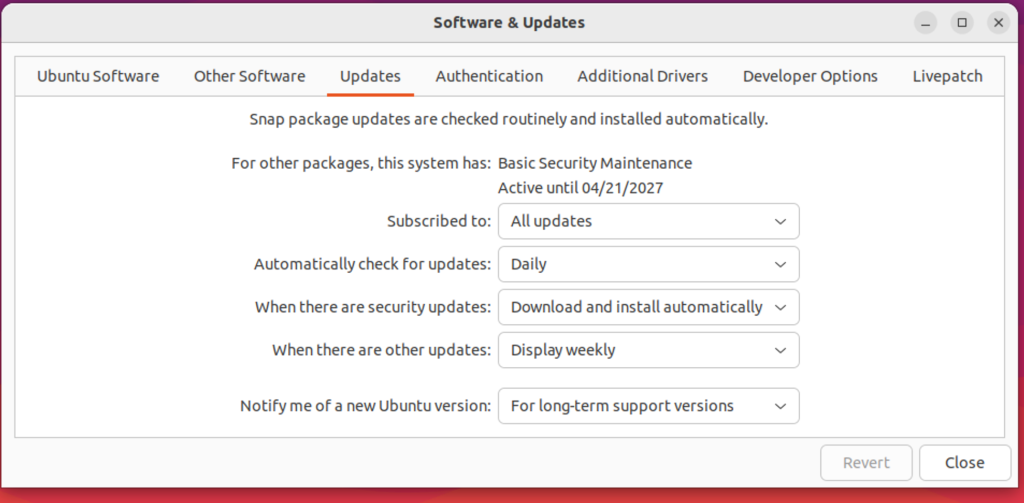
To upgrade to a new version of Ubuntu automatically,
Open the Software & Updates application, and select the Updates tab.
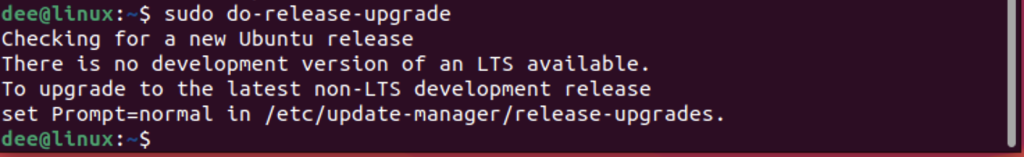
To upgrade to a new version of Ubuntu manually, open the Terminal and type the following command:
sudo do-release-upgrade
Conclusion
Keeping Ubuntu up to date is important for security and stability reasons. There are two ways to keep Ubuntu up to date: via the command line or using the graphical user interface. The quickest and easiest way to keep Ubuntu up to date is via the command line.
