NOTE: Before reading this article, I would like to inform you that the ifconfig command is outdated, and is not recommended anymore. The ip command is the current replacement for the ifconfig command.
Even though this program may be outdated, you may be in a system where you may need this command, so I’ll start with this command.
Linux ifconfig command
This is a network management tool which is used to configure network interfaces. In addition to this, you can also check important internet addresses associated with your system.
This command has various options with it, Let’s look at how we can use these options to look at our network interfaces.
Ifconfig Command Default Usage
By default, you can use this without any arguments. This will display all the network interfaces associated with the system, like wlan and ethernet, along with their status.
ifconfig
The output will look similar to the screenshot below
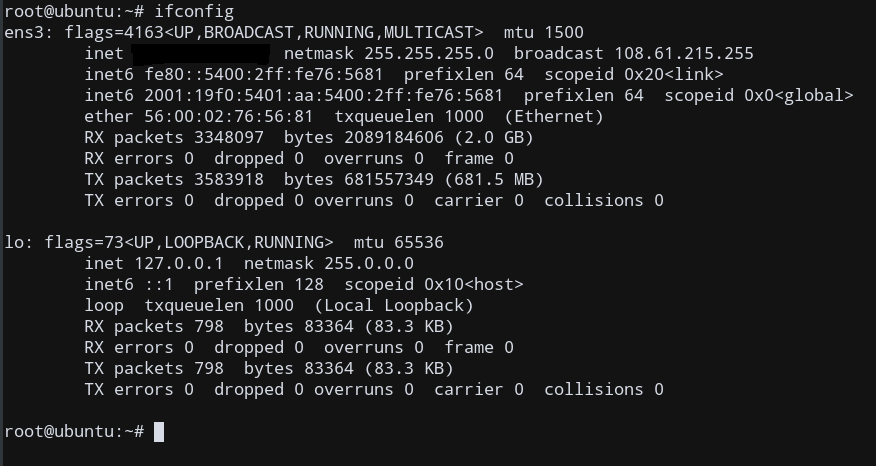
View all Network Interfaces
To view the status of all available network interfaces on the system, using the ifconfig -a command.
ifconfig -a
The output will look similar to the below screenshot
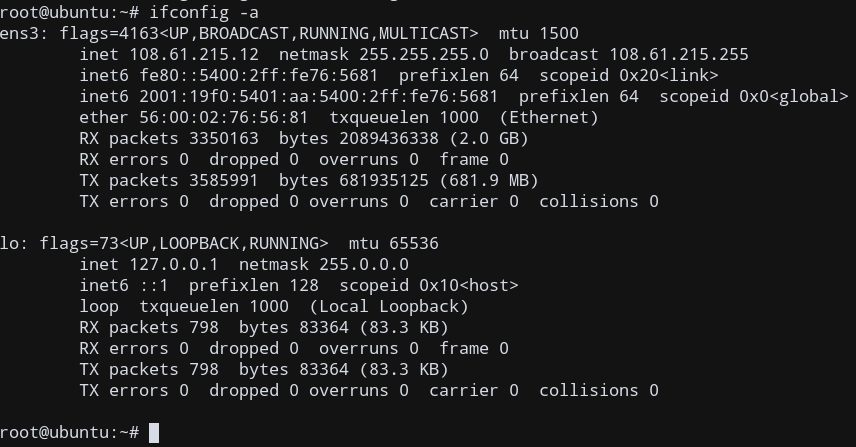
Display ifconfig in a short output
If we want, we can also display the ifconfig output in a short format using the -s option (short)
ifconfig -s
The short output is shown in the below screenshot
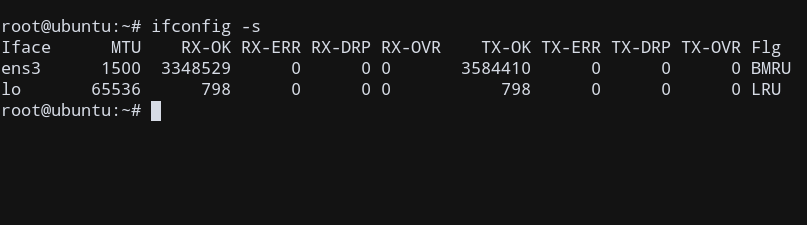
Display contents of a Single Network Interface
In case you specifically want to look at the status of a particular interface, such as enp0s3, or lo we just need to specify the interface name here.
ifconfig lo
This will retrieve the status of the loopback interface, which the local machine uses to communicate with itself.
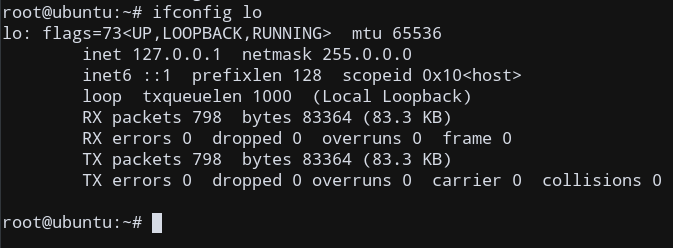
Modify the status of Network Interfaces
We can change the current status of a network interface, by enabling or disabling it using this command.
To enable an interface, add the up option after the interface name
ifconfig enp0s3 up
Similarly, if you wish to bring down an interface, use the down option.
ifconfig enp0s3 down
Enable/Disable Promiscuous Mode
Promiscuous mode is a mode of operation that makes a network adapter to operate with elevated privileges. This means the the network adapter to the interface can now access and look at all packets in a network.
To enable this mode for an interface adapter, type the promisc option after the name of the interface.
ifconfig INTERFACE_NAME promisc
For example, if you wish to make the ens3 interface have elevated privileges, simply type:
ifconfig ens3 promisc
Configure an Interface
We can also use ifconfig to configure an interface. This means that we can explicitly assign new static IP addresses, subnet masks, or even broadcast addresses.
To configure the static IP address and/or the network mask, the command is as follows:
ifconfig INTERFACE_NAME STATIC_IP netmask SUBNET_MASK
Here, INTERFACE_NAME is the name of the required interface to configure. This will assign STATIC_IP along with a SUBNET_MASK on that interface.
For example, if you want to configure the enp0s3 interface, we can do the following:
ifconfig enp0s3 192.168.27.51 netmask 255.255.255.0
This will set the inet address to 192.168.27.51 for that particular interface, along with the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
Modify the MTU value
We can change the value of the mtu (maximum transmission unit), using:
ifconfig INTERFACE_NAME mtu MTU_VALUE
Here, MTU_VALUE is a positive integer, that specifies the new mtu limit.
ifconfig enp0s3 mtu 750
This will set the length of the maximum transmission unit to be 750 bytes.
Conclusion
While the ifconfig command is now outdated, certain scenarios may still require the use of this command. We showed you some of the options involved in viewing and configuring network interfaces using this command.
References
- JournalDev article on the
ifconfigcommand
