Most Windows users who migrate to Linux are surprised to find that the task manager works differently. On Windows, the task manager is accessed by pressing the Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination. However, in Linux systems, the type of task manager depends on the Desktop Environment being used.
The GNOME Desktop Environment, which is shipped with Ubuntu, Fedora, and Manjaro, has an application called the ‘System Manager’. This contains all system-related information such as RAM usage, Bandwidth usage, and a list of all running processes.
In this article, we will take a look at the System Monitor, which is GUI based, and the Terminal application Htop, which serves the same purpose.
System Monitor – The GUI Task Manager in GNOME
System monitor is a nifty little application that allows you to keep an eye on your computer’s performance. To access it, simply press the Super key (Windows Key) on your keyboard and look for the icon. Once you’ve found it, either click on the icon or press Enter to launch the program.
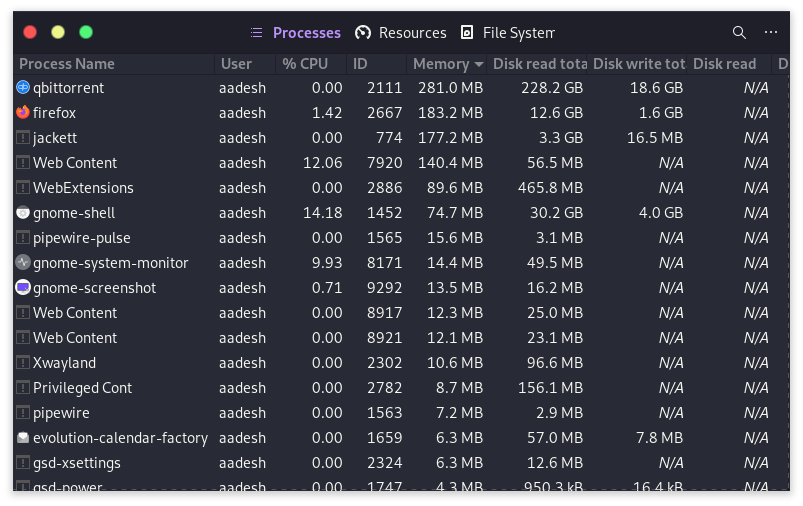
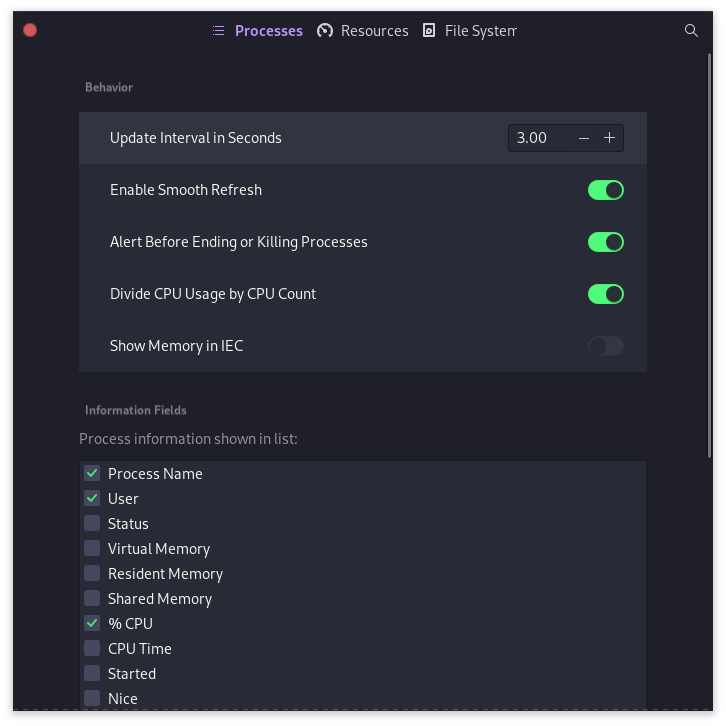
The System Monitor tool has three sections: Processes, Resources, and File Systems. In the Processes tab, you can see all the running processes and quickly end them by pressing Ctrl+K or clicking the bottom button. This is a handy way to keep your computer’s performance up and manage its memory usage.
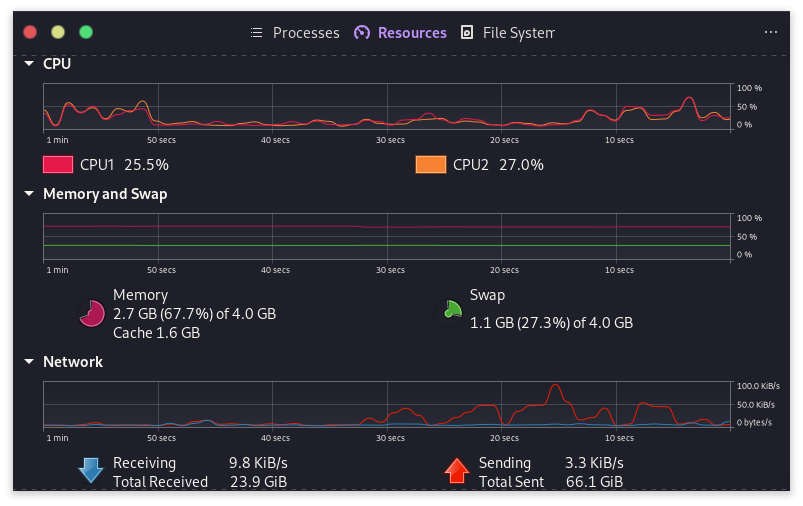
In the second Resources tab, you can find system usage information like RAM and Swap, CPU, and bandwidth. This is helpful for data monitoring if you have a data cap on your internet connection. By monitoring your usage, you can avoid exceeding your limit and incurring additional charges.
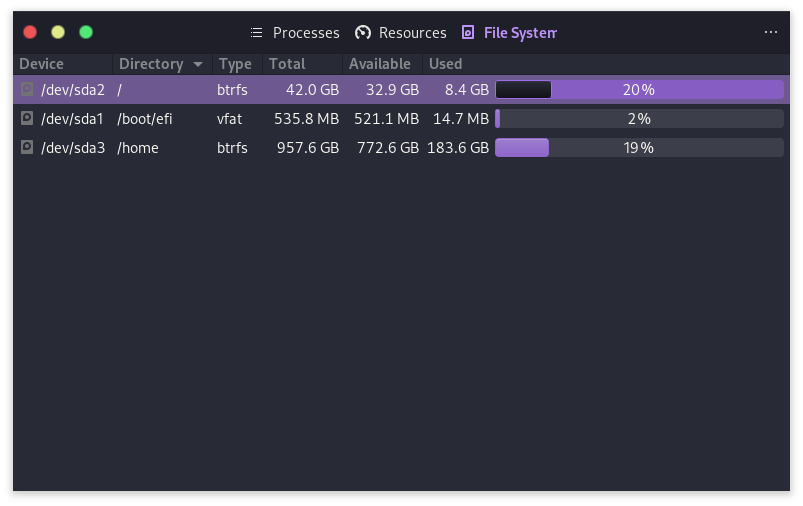
The File System in Windows shows you all the disks currently attached to your PC, as well as the amount of space used and free on each one. It also lists the mount point for each partition. This can be useful when trying to figure out why your hard drive is full, or where a particular file is located.
In the hamburger menu on the top right, you can select which fields to be displayed in the mentioned 3 tabs. By default, various fields are already selected, but you can always add or remove fields as you see fit. This way, you can easily tailor the information in the tabs to your liking!
Htop – The CLI Task Manager
Htop is one of the most popular CLI-based task managers. Although it might not be installed by default on many distributions, the installation process is easy. Simply open your terminal and use your package manager (apt, dnf, pacman, etc.) to install it.
In Ubuntu/Debian based distributions :
sudo apt update && sudo apt install htop
In Manjaro and Arch based distributions :
sudo pacman -S htop
And on Fedora and RHEL based systems :
sudo dnf/yum install htop
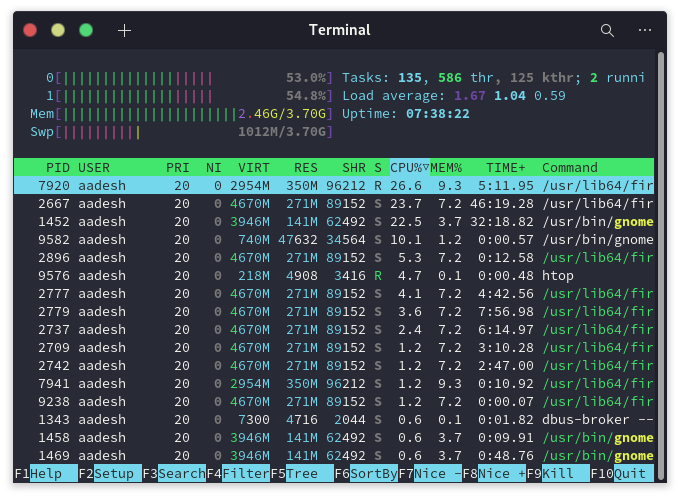
To launch Htop, simply open a Terminal window and type Htop, and press enter. To know more about the functionality of Htop, you can read this article, where the command has been discussed in detail.
Summary
There are multiple ways to manage all the running processes and monitor the system-resource usage on Linux. While the names of the programs may be different from what Windows users are used to, with a little bit of exploration any user can find the right program for their needs. With so many options available, users are sure to find the perfect way to keep track of their system’s performance.
