In this article, we will be comparing Ubuntu vs Opensuse and will see which one is best suited for you. Deciding which is the best Linux distro completely depends on the user’s needs.
Ubuntu vs Opensuse
Ubuntu is a free and open-source operating system suitable for both beginners and advanced users. It was released in 2004 by Canonical Ltd. It is a very popular distro as it is very user-friendly and its long-term support. It has three editions:-
- Ubuntu Desktop
- Ubuntu Server
- Ubuntu Core
OpenSUSE is an Open-source operating system developed by OpenSUSE Project and was released in 2005. OpenSUSE is also called ‘The Maker’s choice’ for system admins, desktop users, and developers. OpenSUSE has two versions:
- OpenSUSE Leap
- OpenSUSE Tumbleweed
Let’s discuss the differences between Ubuntu and OpenSUSE on the following factors:
1. Installation – Ubuntu vs Opensuse
Ubuntu is very easy to install, even for beginners. It comes with a graphical installer and the process is quite straightforward. It is called ‘Linux for Human Beings’. For users who are switching to Linux from Windows or Mac, Ubuntu is the best option.
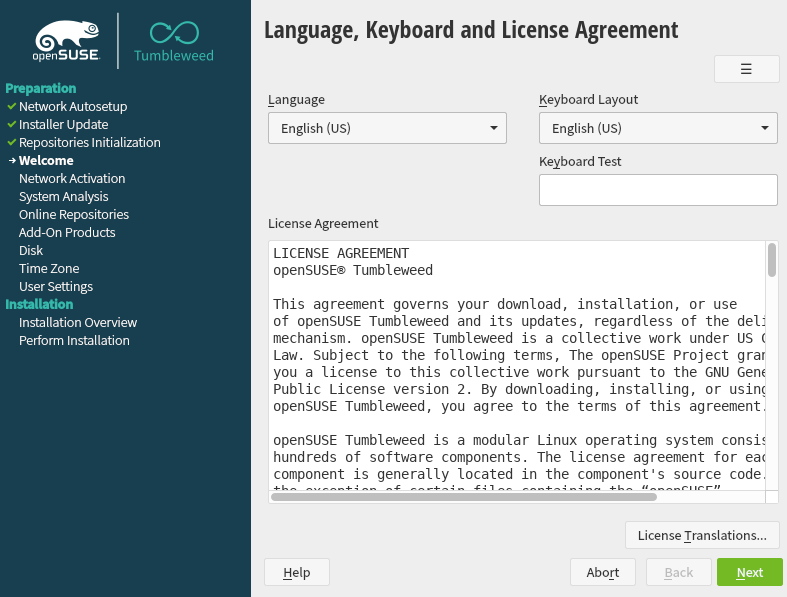
As compared to Ubuntu, OpenSUSE is a bit complicated in the case of installation. While partitioning disks, it gives an option to choose from a list of plans for partitioning and that makes it too confusing.
2. Desktop Environment – Ubuntu vs Opensuse
Ubuntu comes with GNOME installed by default. However, It supports many other desktop environments like Budgie, LXDE, Cinnamon, Mate, Xfce, etc. You can install other Desktop environments manually if you want. GNOME is a very good desktop environment used by many Linux distros. Though, It does not have a lot of customization but gives a good look and feel.
OpenSUSE also uses the GNOME desktop environment by default. During installation, you have to choose from GNOME and KDE. It also supports other desktop environments like Cinnamon, Mate, Xfce, etc. You need to install them manually. Both use the same desktop environment so it depends on you which gives you a better feel.
3. Package Manager – Ubuntu vs Opensuse
Ubuntu is based on Debian so it mainly works with the .DEB packages. It has many package managers. First, Snap and APT are the two package managers used for installing, managing, and removing the packages. It also uses Synaptics which comes with a great UI that does not require writing any command to install packages.
OpenSUSE, on the other hand, comes with RPM and Zypper that are command-line package managers to handle basic package management. YaST is another package manager used by OpenSUSE. It is mainly used for OS installation. It gives a very good feeling, especially for beginners who are not so familiar with command lines.

4. Release Cycle – Ubuntu vs Opensuse
Ubuntu rolls out its ‘Long Term Support’ (LTS) releases every two years in April. The latest Long Term Support version is Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. It also rolls out its interim releases every six months but they don’t get long-term support.
OpenSUSE has two variants: OpenSUSE Leap and OpenSUSE Tumbleweed.
- OpenSUSE Leap has a rolling release that always remains updated to the latest release.
- OpenSUSE Tumbleweed rolls out its releases every 12 months (minor release) and every 36-48 months (major release).
Both Ubuntu and OpenSUSE are stable, reliable and gives better performance though OpenSUSE is more stable and also very lightweight for servers.
5. System Requirements – Ubuntu vs Opensuse
Ubuntu is compatible with almost all devices and has modest system requirements. It recommends a minimum of 2GB RAM, 25GB Storage, and a 2GHz dual-core processor. If you have an old device with low hardware, You can install Xubuntu or LUbuntu which are lightweight desktop systems.
OpenSUSE is not so popular as it should be, It still has many users. It requires a minimum of 1GB RAM (However, 2GB RAM is recommended), 10GB storage for minimal installation and 16GB storage is recommended for Graphical installation, and Pentium 4.1GHz processor ( or AMD64 or Intel64 processor).
6. Community Support – Ubuntu vs Opensuse
Ubuntu has very large community support, It provides various sources like Ubuntu Wiki, Ubuntu Forums, and Ask Ubuntu. There are many other community forums so no need to worry if you are stuck somewhere.
OpenSUSE also has a very active user community and forums. It offers official documentation, Support, OpenSUSE community, OpenSUSE Forums. Both Ubuntu and OpenSUSE have very active community support.
Conclusion
We have discussed the key differences between Ubuntu and OpenSUSE on various factors. Now, It completely depends on your requirements that which is best suited for you. If you have a home computer or you are a beginner, Ubuntu is the best option. OpenSUSE is quite hard to learn as compared to Ubuntu. However, both are the best Linux distributions among all the Linux distros.
FAQs
What is the main difference between Ubuntu and OpenSUSE as linux distributions?
The primary difference lies in their package management systems and default desktop environments. Ubuntu typically uses APT for package management, while OpenSUSE utilizes Zypper and YaST. Ubuntu defaults to GNOME, whereas OpenSUSE’s primary desktop is KDE, which offers a different user interface experience.
How can I install Ubuntu or OpenSUSE on my laptop?
To install Ubuntu, you can download the ISO from the official website and create a bootable USB stick. For OpenSUSE, you can do the same by downloading the version of OpenSUSE that suits your needs (Leap or Tumbleweed). Both distributions offer comprehensive installation guides on their respective websites.
Which operating system is better for new users, Ubuntu or OpenSUSE?
Generally, Ubuntu is considered more user-friendly for new users due to its extensive community support and documentation. However, OpenSUSE is also a great option, especially for users who want to delve into more advanced features like YaST for system configuration.
Does OpenSUSE support the same software packages as Ubuntu?
While both Ubuntu and OpenSUSE are based on the Linux kernel and have access to a wide range of open-source software, the package formats differ. Ubuntu uses .deb packages, while OpenSUSE uses .rpm packages. Some software may need to be recompiled or specifically packaged for each distribution.
Can I use OpenSUSE alongside Ubuntu on the same machine?
Yes, you can dual-boot both operating systems on the same machine. This setup allows you to choose which linux distribution to boot into at startup. When configuring your partitions, make sure to allocate enough space for each operating system and any shared data.
What are the graphical user interface options available in Ubuntu and OpenSUSE?
Ubuntu primarily uses the GNOME desktop environment, which focuses on simplicity and ease of use. OpenSUSE offers several desktop environments, with KDE being the default, which is highly customizable and feature-rich. Users can choose to install other environments like XFCE or GNOME on both distributions.
How does package management differ between Ubuntu and OpenSUSE?
Ubuntu uses the APT package management system, which allows for easy installation and updating of software packages through the command line or GUI tools like Software Center. OpenSUSE employs Zypper and YaST, offering powerful package management capabilities, including system configuration and management tools.
Which linux distribution is more suitable for gaming, Ubuntu or OpenSUSE?
Generally, Ubuntu is favored for gaming due to its broader support for gaming applications and drivers, including proprietary graphics drivers. However, OpenSUSE can also be configured for gaming, but it may require more manual setup to achieve the same level of compatibility.
Are there any specific advantages of using OpenSUSE over Ubuntu?
OpenSUSE offers advanced system management tools like YaST and better support for certain server applications. Additionally, its rolling release model in Tumbleweed provides the latest software versions, which can be beneficial for users who want cutting-edge features.
Can I run OpenSUSE on systems with limited resources compared to Ubuntu?
Yes, both OpenSUSE and Ubuntu have lightweight versions. OpenSUSE offers a minimal installation option, and Ubuntu has flavors like Xubuntu or Lubuntu that are tailored for low-resource environments. Users can select the one that best meets their system capabilities and personal preferences.
